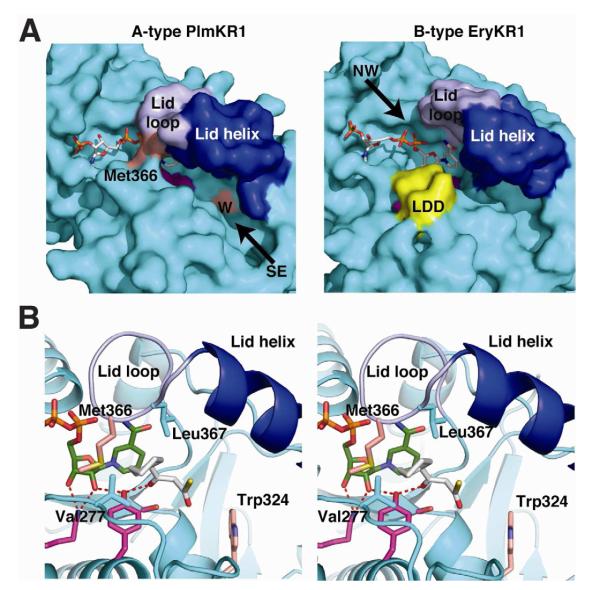
Figure 4. Comparison of A-type and B-type KRs.
(A) Stereo view of PlmKR1 (cyan) and SpnKR2 superposition (white, PDB code: 3SLK) (RMSD = 1.187 Å). The active site tyrosine and the NADP(H) are in different positions in the A-type (PlmKR1, cyan) and B-type (SpnKR2, white) KRs. In PlmKR1, the hydrogen bond network of Lys297, ribose 2′-hydroxy and Tyr332 is shown as red dashes, and the hydrogen bond network of nicotinamide amide, lid loop, and NADP+ β-phosphate as yellow dashes. The PlmKR1 catalytic residues are drawn in stick form with magenta C and the NADPH cofactor with green C, and the EryKR1 NADPH was omitted because of disorder.
(B) Schematic of the hydrogen bond network of NADP+ bound to the A-type PlmKR1. In cofactor complexes of B-type KRs, only the hydrogen bonds of Lys to ribose 2′-hydroxy and of nicotinamide amide to NADP(H) β-phosphate have been observed.