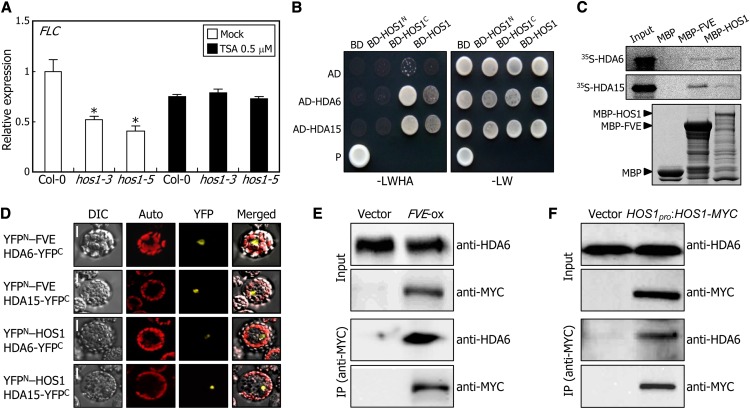
Figure 5.
HOS1 Interacts with HDA6 in the Nucleus.
(A) Effects of TSA on FLC expression. Plants were grown for 10 d on MS-agar plates containing 0.5 μM TSA. The levels of FLC mRNA were determined by qRT-PCR. Biological triplicates were averaged for each plant genotype and statistically treated (Student’s t test, *P < 0.01). Bars indicate se.
(B) Interactions of HOS1 with HDA6 and HDA15 in yeast cells. The HDA6 and HDA15 genes were fused in frame to the GAL4 AD-coding sequence. The HOS1 constructs used were as described in Figure 3B.
(C) In vitro pull-down assays. Recombinant MBP-FVE and MBP-HOS1 fusions as well as in vitro–translated, 35S-labeled HDA6 and HDA15 polypeptides were used (top and middle panels, respectively). Part of a Coomassie blue–stained gel is shown (bottom panel).
(D) BiFC assays. Partial YFP fusion constructs were coexpressed transiently in Arabidopsis protoplasts and visualized by differential interference contrast microscopy (DIC) and fluorescence microscopy. Bars = 20 μm.
(E) and (F) in vivo interaction of HDA6 with FVE (E) and HOS1 (F). Total proteins extracted from the FVE-ox and HOS1pro:HOS1-MYC transgenic plants grown for 6 d were immunoprecipitated with anti-MYC agarose beads. The FVE, HOS1, and HDA6 proteins were detected immunologically using an anti-MYC or anti-HDA6 antibody.