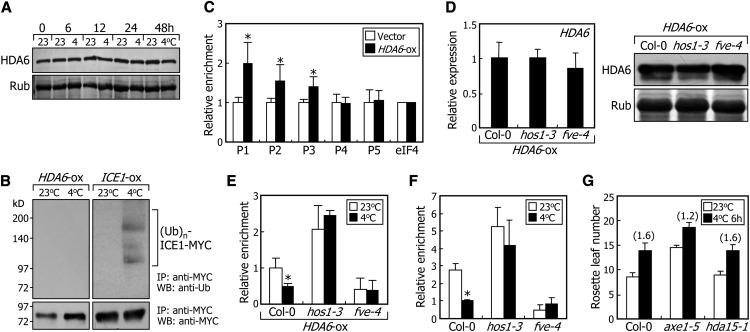
Figure 6.
Cold Stress Attenuates Binding of HDA6 to FLC Chromatin.
(A) Effects of cold stress on HDA6 protein stability. Ten-day-old transgenic plants overexpressing a HDA6-MYC gene fusion under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter (HDA6-ox) were exposed to 4°C for the indicated time. Whole plants were harvested for preparation of protein extracts. The levels of HDA6 were compared immunologically using an anti-MYC antibody. Parts of Coomassie blue–stained gels containing the ribulose-1,5-bis-phosphate carboxylase/oxygenase protein are shown at the bottom.
(B) Effects of cold stress on HDA6 ubiquitination. Ten-day-old HDA6-ox transgenic plants were used in the ubiquitination assays. Total protein was immunoprecipitated with an anti-MYC antibody and analyzed immunologically using anti-MYC and anti-ubiquitin antibodies. Transgenic plants overexpressing the ICE1-MYC gene fusion (ICE1-ox) were also analyzed for comparison. IP, immunoprecipitation assay. WB, protein gel blot analysis.
(C) Binding of HDA6 to FLC chromatin. The HDA6-ox transgenic plants were grown on MS-agar plates for 2 weeks before harvesting of plant materials. ChIP assays were performed using an anti-MYC antibody, as described in Figure 1. Biological triplicates were averaged and statistically treated using Student’s t test (*P < 0.01). Bars indicate se.
(D) Relative levels of HDA6 protein and HDA6 mRNA in HDA6-ox transgenic plants in different genetic backgrounds. The mRNA levels were examined by qRT-PCRs (left panel). Biological triplicates were averaged and statistically treated (t test, *P < 0.01). Bars indicate se. The levels of HDA6 were determined immunologically using an anti-MYC antibody (right panel).
(E) Effects of cold stress on HDA6 binding to FLC chromatin. ChIP assays were performed as described in Figure 1, using an anti-MYC antibody. Chromatin extracts from plant materials described in (D) were used. Ten-day-old plants grown on MS-agar plates at 23°C were further grown at either 23 or 4°C for 2 d before harvesting of plant materials. The P1 sequence region of the FLC chromatin, as shown in Figure 1C, was used in the ChIP assays. Biological triplicates were averaged and statistically treated (t test, *P < 0.01). Bars indicate se.
(F) Binding of HDA6 to FLC chromatin in the hos1-3 and fve-4 mutants. ChIP assays were performed as described in Figure 1, using an anti-HDA6 antibody. Chromatin extracts from Col-0 plants and hos1-3 and fve-4 mutants were used. Conditions for cold treatments were identical to those described in (E). Biological triplicates were averaged and statistically treated (t test, *P < 0.01). Bars indicate se.
(G) Effects of intermittent cold on flowering time. Intermittent cold treatments and measurements of flowering times were performed as described in Figure 2. The numbers in parentheses refer to the ratios of rosette leaf numbers with and without intermittent cold treatments.