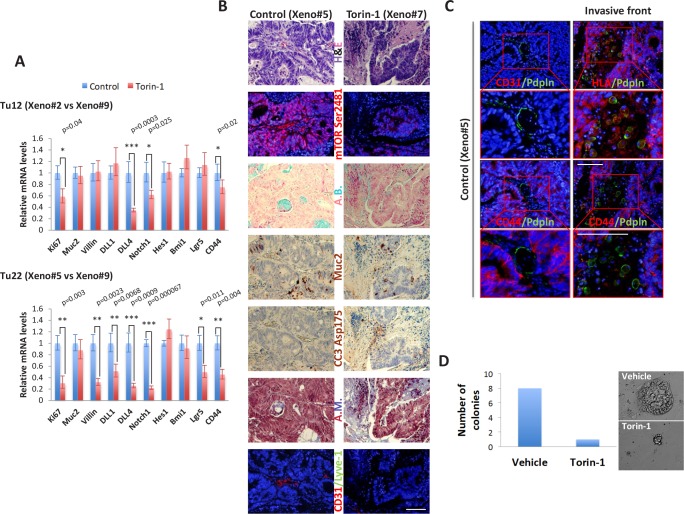
Figure 7. Torin-1 decreases the expression of proliferative, angio-/lympho-genic, and stem cell markers, and activates apoptosis in vivo.
(A) Bar graphs showing relative real-time qPCR analysis of Ki67, Muc2, Villin, DLL1, DLL4, Notch1, Hes1, Bmi1, Lgr5, and CD44 in control or Torin-1-treated Tu12 (Xeno#2 vs Xeno#9, upper) or Tu22 (Xeno#5 vs Xeno#9, lower) tumors. Expression was normalized to GAPDH mRNA. Error bars represent upper and lower error limits based on replicate variability (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001). (B) Images of PFA-fixed, paraffin-embedded serial sections of control or Torin-1-treated Tu22 tumors (Xeno#5 vs Xeno#7) stained with H&E, mTOR Ser2481, Alcian Blue (A.B.), Muc2 (AEC, red color), cleaved caspase-3 (CC3) Asp175 (AEC, red color), Azan Mallory (A.M.), or CD31/Lyve-1. Scale bar, 100μm. (C) Immunofluorescence pictures of control Tu22 tumor (Xeno#5) sections showing Podoplanin (Pdpln) expression in both lymphatic vessels (left) and tumor cells (right) at the invasive front. Scale bars, 100μm. Podoplanin+ vessels were CD31−. The human origin of Podoplanin+ cells located outside vessels was confirmed by HLA staining. Podoplanin+ cells exhibited round morphology and were CD44−. (D) Bar graphs showing number of colonies generated from CD326+ cells isolated from vehicle or Torin-1-treated xenografts. 103 cells were plated on a 24-well plate previously coated with LA7 feeder layer cells, and grown for 1 week before scoring the number of colonies.