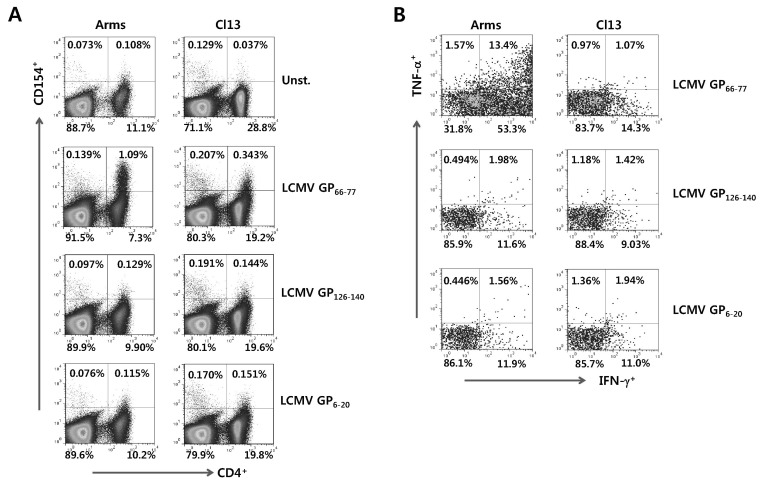
Figure 2.
Detection of LCMV-specific CD4+ T cells by intracellular CD154 staining. (A) Detection of viable LCMV-specific CD4+ T cells by intracellular CD154 staining. The splenocytes from mice infected with LCMV Arms or Cl13 were prepared 7 days pi and simulated with each specific epitope peptide (LCMV GP66-77, GP126-140, and GP6-20) in presence of PE-conjugated anti-CD154 antibody for 12 h. Splenocytes that was not stimulated with peptide in the presence of PE-conjugated anti-CD154 antibody were used for negative control. The values in dot-plot represent the percentage of CD4+ T cells specific for each LCMV epitope peptide. (B) The profile of IFN-γ and TNF-α expression in LCMV Ag-specific CD4+ T cells detected by intracellular CD154 staining. Following 12 h-stimulation of each epitope peptide in the presence of PE-conjugated CD154 antibody, the cells were stained with anti-CD4 antibody and the expression of IFN-γ and TNF-α in CD154+CD4+ T cells was determined by intracellular cytokine staining. The values in dot-plot represent the average percentage of IFN-γ and TNF-α in CD154+CD4+ T cells.