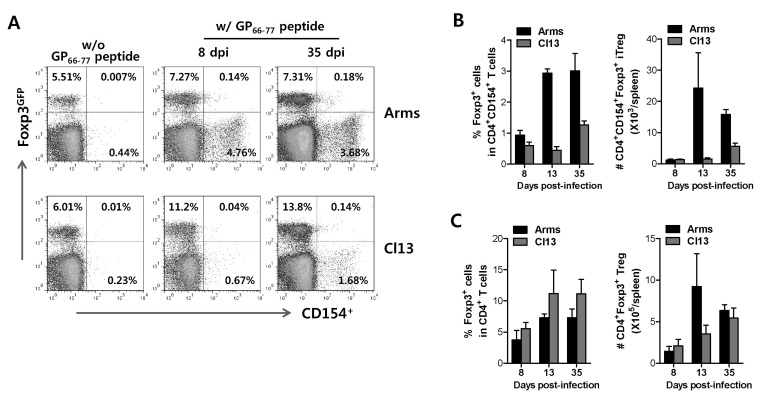
Figure 4.
Differential expansion of LCMV GP66-77-specific CD4+Foxp3+ iTreg and CD4+Foxp3+ Treg in acute and chronic infection. (A) Frequency of LCMV GP66-77-specific CD4+CD154+Foxp3+ iTreg in acute and chronic LCMV infection. Foxp3GFP knock-in mice were infected with LCMV Armstrong (Arms) or clone 13 (Cl13) and the splenocytes from LCMV-infected Foxp3GFP knock-in mice were prepared 8 and 35 days pi and used for 12 h-stimulation with LCMV GP66-77 epitope peptide in the presence of PE-conjugated anti-CD154 antibody. The values in dot-plot denote the average of CD154+Foxp3- Th, CD154-Foxp3+ Treg, CD154+Foxp3+ iTreg cells gated on CD4+ T cells (B and C) The frequency and absolute number of LCMV GP66-77-specific CD4+CD154+Foxp3+ iTreg and nonspecific CD4+Foxp3+ Treg cells. The splenocytes of infected Foxp3GFP knock-in mice were prepared 8, 13 and 35 days pi, stimulated with LCMV GP66-77 in the presence of the presence of PE-conjugated anti-CD154 antibody. The bars in graphs represent the average±SD of LCMV GP66-77-specific CD4+CD154+Foxp3+ iTregs (B) and nonspecific CD4+Foxp3+ Treg (C) detected by intracellular CD154 staining in acute and chronic phase.