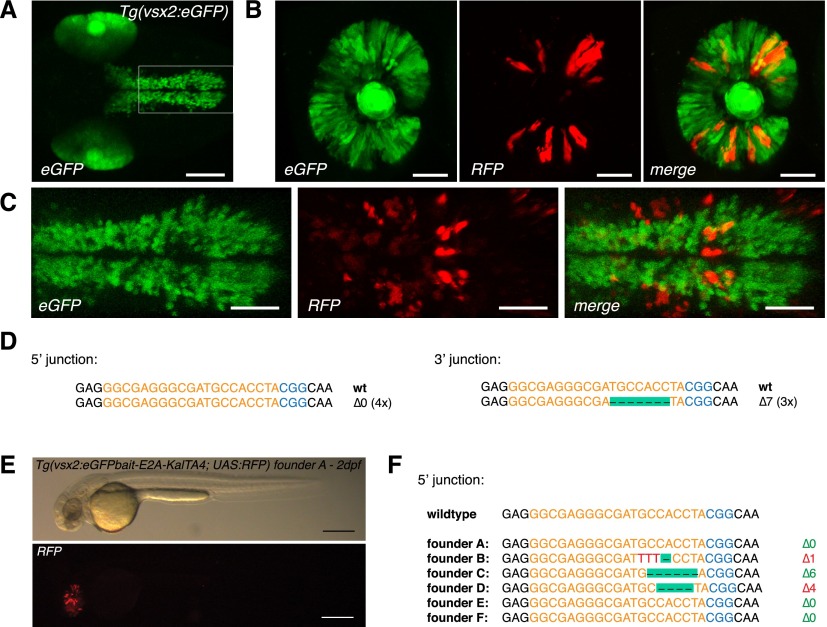
Figure 2.
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knock-in of KalTA4 into the Tg(vsx2:eGFP) transgenic line. (A) Tg(vsx2:eGFP) shows eGFP expression in retina progenitor cells and the hindbrain region in 2dpf transgenic embryos. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) eGFP to KalTA4 conversion in retina progenitor cells of Tg(vsx2:eGFP) × Tg(UAS:RFP, cry1:eGFP) embryos as revealed by RFP expression. The same donor plasmid and sgRNA eGFP 1 as in Figure 1 were used. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) eGFP to KalTA4 conversion was seen as well in the developing hindbrain. Zoom-in of region indicated in A. Scale bar, 50 μm. (D) Using PCR, the targeted integration events could be verified. Sequence analysis of the 5′ junction and the 3′ junction. (E) F1 embryo (from founder A) with stable expression of the Tg(vsx2:eGFPbait-E2A-KalTA4, UAS:RFP) transgene activating RFP expression from UAS:RFP in the retina. Scale bar, 300 μm. (F) List of 5′ junctions of alleles identified in stable transgenic founders. Within 12 screened potential founder fish, six alleles could be detected, whereas four founders showed in-frame integration of the transgene. (Orange) sgRNA binding site; (blue) PAM sequence NGG.