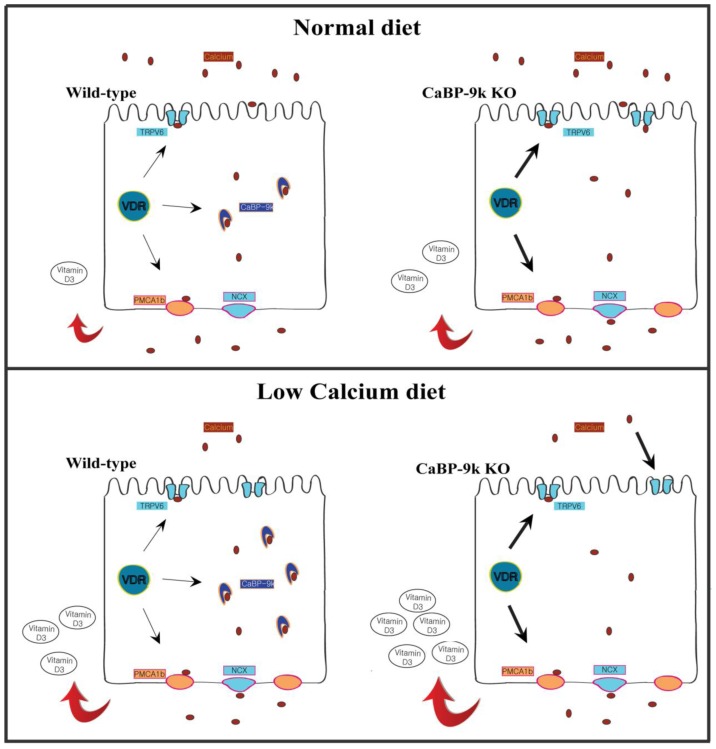
Figure 3.
The role of CaBP-9k in the extracellular and intracellular environment of enterocytes. In calcium absorption, the abolishment of intracellular CaBP-9k stimulates compensative increase of vitamin D, and the increased vitamin D induces the expression of apical or basolateral membrane bound channels. In addition, a low calcium diet may also stimulate the expression of membrane bound channels in CaBP-9k knockout mice.