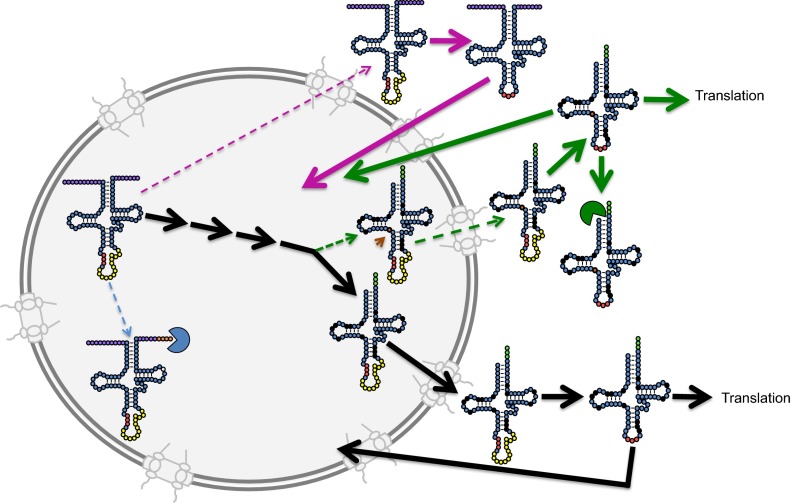
Fig. 4.
Interactions of tRNA quality control pathways. tRNA processing/trafficking pathways are color coded. Black arrows indicate the canonical pathway leading to mature cytoplasmic tRNAs that participate in translation. Blue dotted arrow indicates aberrant 3′ processing; the aberrant transcript is destroyed by the 3′–5′ exosome quality control pathway (blue packman). Pink dotted arrow indicates precocious nuclear export before 5′ and 3′ processing; aberrant transcripts are spliced in the cytoplasm and return to the nucleus via retrograde nuclear import (long solid pink arrow). Green dotted arrows indicate precocious nuclear export before complete modification in the nucleus; solid green arrows demonstrate that hypomodified tRNAs are spliced in the cytoplasm and may participate in translation or may be destroyed by the 5′–3′ RTD exonuclease, Xrn1 (green packman), or may return to the nucleus via retrograde import (long solid green arrow), followed by repair or destruction by the nuclear RTD exonuclease. Orange arrow indicates the tRNA position normally modified by m22G26; the nucleotide missing this modification is indicated by a solid orange circle.