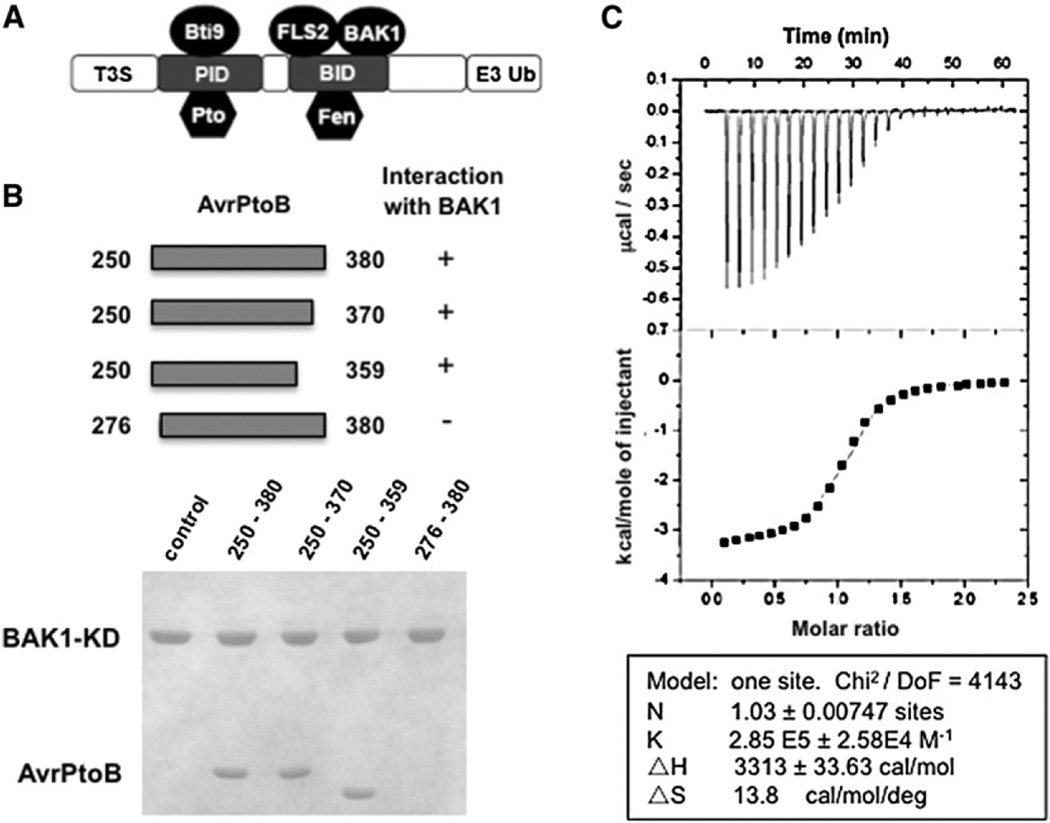
Figure 1. AvrPtoB250–359 Is Sufficient for Interaction with the BAK1 Kinase Domain.
(A) A schematic diagram of the structural organization of AvrPtoB. T3S, type III secretion sequence; PID, Pto-interacting domain; BID, BAK1-interacting domain; E3 Ub, E3 ubiquitin ligase.
(B) The upper panel depicts the AvrPtoB fragments tested for interaction with BAK1-KD (residues 250–591). Each AvrPtoB fragment was individually incubated with BAK1-KD and subjected to gel filtration analysis. Aliquots of the peak fraction corresponding to BAK1-KD were visualized by Coomassie blue staining following SDS-PAGE, as observed in the lower panel.
(C) Quantification of binding affinity between BAK1-KD and BID by isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC). Twenty-four injections of AvrPtoB250–359 solution were added to the BAK1-KD protein solution in the ITC cell. The area of each injection peak corresponds to the total heat released for that injection. The integrated heat is plotted against the molar ratio of AvrPtoB250–359 added to BAK1-KD in the cell. Data fitting revealed a binding affinity of 3.5 µM.