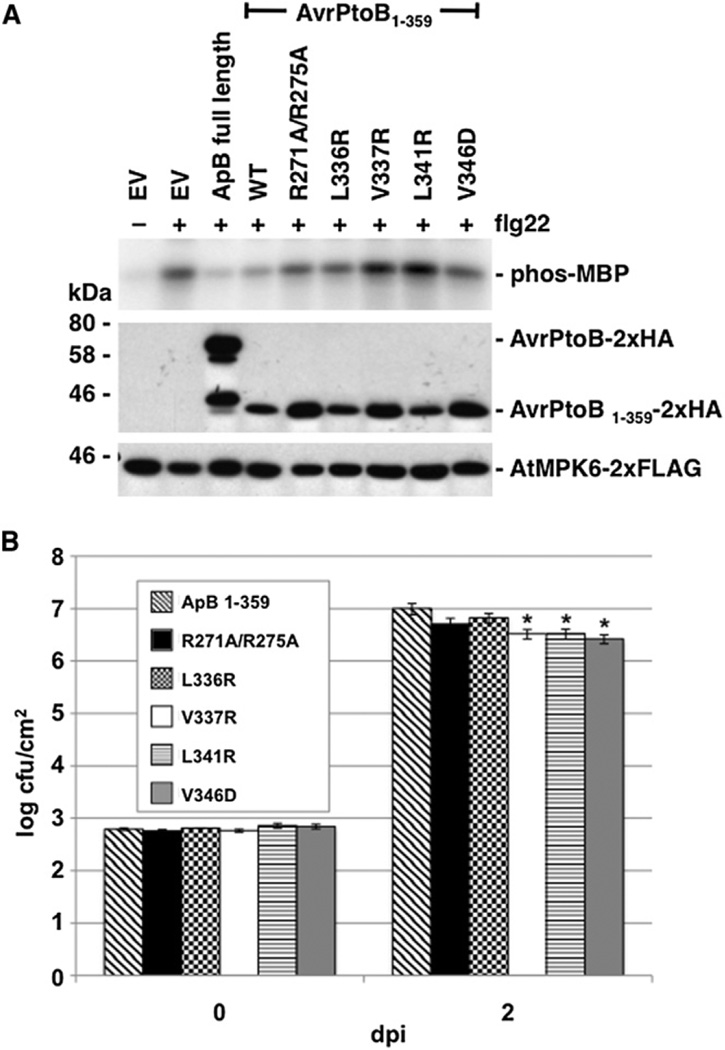
Figure 6. Mutant Forms of AvrPtoB1–359 Unable to Interact with BAK1-KD In Vitro Are Impaired in Virulence.
(A) AvrPtoB (ApB) variants unable to interact with BAK1-KD in vitro have reduced ability to suppress MPK6 activation in Arabidopsis Col-0 protoplasts. Protoplasts expressing AtMPK6 and AvrPtoB were treated with 1 µM flg22 for 10 min. AtMPK6 activity was assessed in an immunocomplex kinase assay with MBP as the substrate (upper panel shows autoradiograph). AtMPK6 and AvrPtoB protein abundance were detected by immunoblot analysis (middle and lower panels). The smaller protein in the full-length AvrPtoB lane is probably a degradation product of the effector.
(B) AvrPtoB variants unable to interact with BAK1-KD in vitro have reduced virulence in tomato. Pst DC3000 ΔavrPtoΔavrPtoB strains expressing AvrPtoB1–359 wild-type or its variants were vacuum infiltrated into RG-prf-3 leaves at 3 × 104 cfu/ml. Bacterial growth per leaf area was determined at 0 and 2 days postinoculation (dpi). The figure is derived from data from one representative experiment using four biological replicates per strain. *Significantly different from wild-type at p < 0.05. The statistical analysis was performed on data derived from seven experiments, analyzed as the fold increase between days 0 and 2, using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD as the correction; bars represent ± standard error (see also Figure S4 and Table S2).