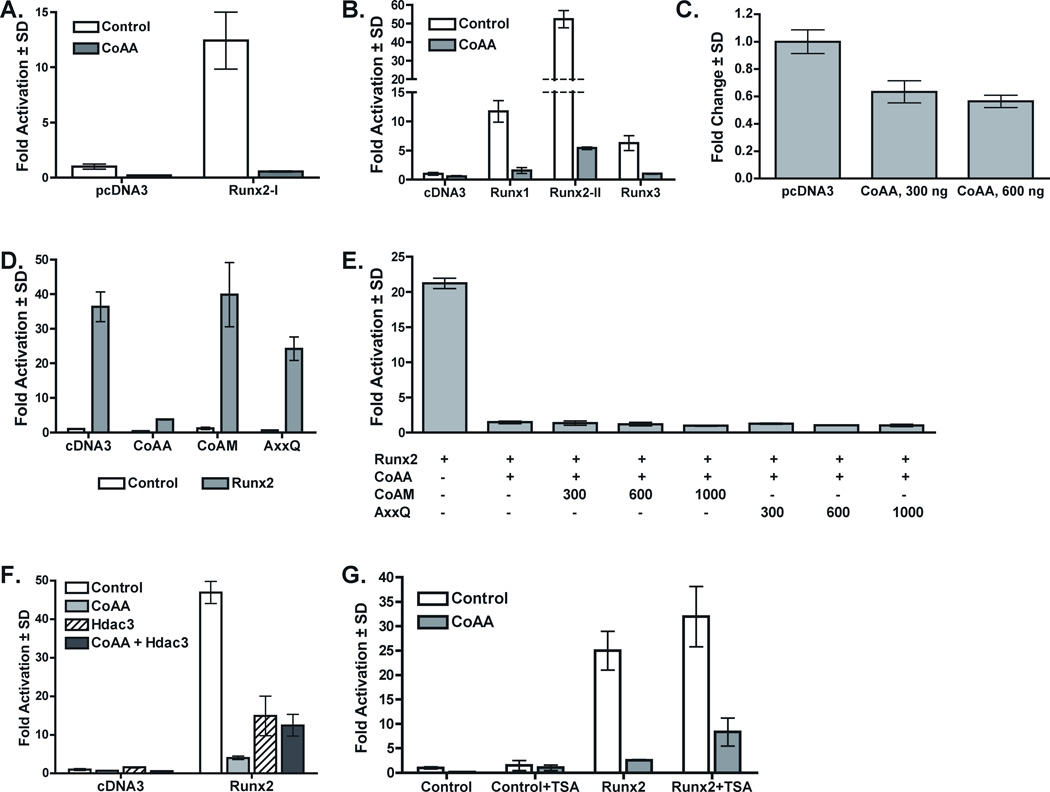
Figure 4. CoAA Represses Runx Factor Transcriptional Activity in a Histone Deacetylase Independent Manner.
The effects of CoAA on Runx factor transcriptional activity were performed in C2C12 cells co-transfected with p6OSE2-luciferase or mOG2-luciferase, pRenilla luciferase and, unless otherwise noted, 300 ng of the indicated expression plasmids. Empty pcDNA3 was added to equalize DNA amounts transfected into cells. Firefly luciferase levels were normalized to renilla luciferase levels. Results represent the mean of triplicate samples. A. CoAA blocks Runx2-I (begins with amino acids MRIPV)-dependent activation of p6OSE2. B. CoAA blocks Runx1, Runx2-II (begins with residues MASNSL), and Runx3-induced activation of p6OSE2. C. CoAA blocks the basal activity of the mouse osteocalcin promoter (mOG2)-luciferase. D. Runx2-II-dependent activation of p6OSE2-luciferase is completely blocked by CoAA, but not by CoAM. CoAA-AxxQ mutant constructs partially inhibit Runx2-II-dependent activation. E. Neither CoAM nor AxxQ inhibits CoAA-mediated repression of Runx2-II-driven p6OSE2-luciferase. F. Hdac3 and CoAA repress Runx2-II activity, but do not synergize to repress Runx2-II. E. The Hdac inhibitor, trichostatin A (TSA) was added to cell culture during the last 18 hours of incubation. TSA increases Runx2-II-dependent activation of p6OSE2-luciferase but did not relieve CoAA repression of Runx2-II.