Figure 1.
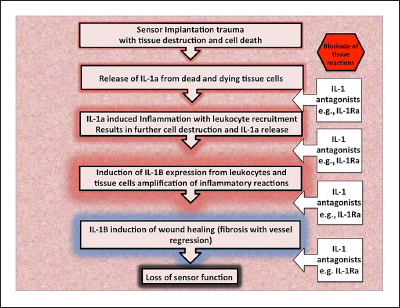
General model of the role of IL-1 (IL-1a and IL-1B) and IL-1Ra in glucose sensor induced tissue reactions. This model illustrates the cascade of IL-1-related events from the release of IL-1 from damaged tissues to loss of sensor function. At each step following the release of internal cellular IL-1a due to sensor implantation trauma, IL-1Ra can inhibit the cascade. Interleukin-1a release from damaged tissues induces further IL-1 alpha inflammation and cell destruction with leukocyte recruitment. Interleukin-1 beta is expressed by the leukocytes, leading to other inflammatory reactions and ultimately wound healing processes, including fibrosis with vessel regression, a severe inhibitor of accurate and timely sensor function.
