Abstract
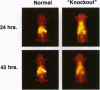
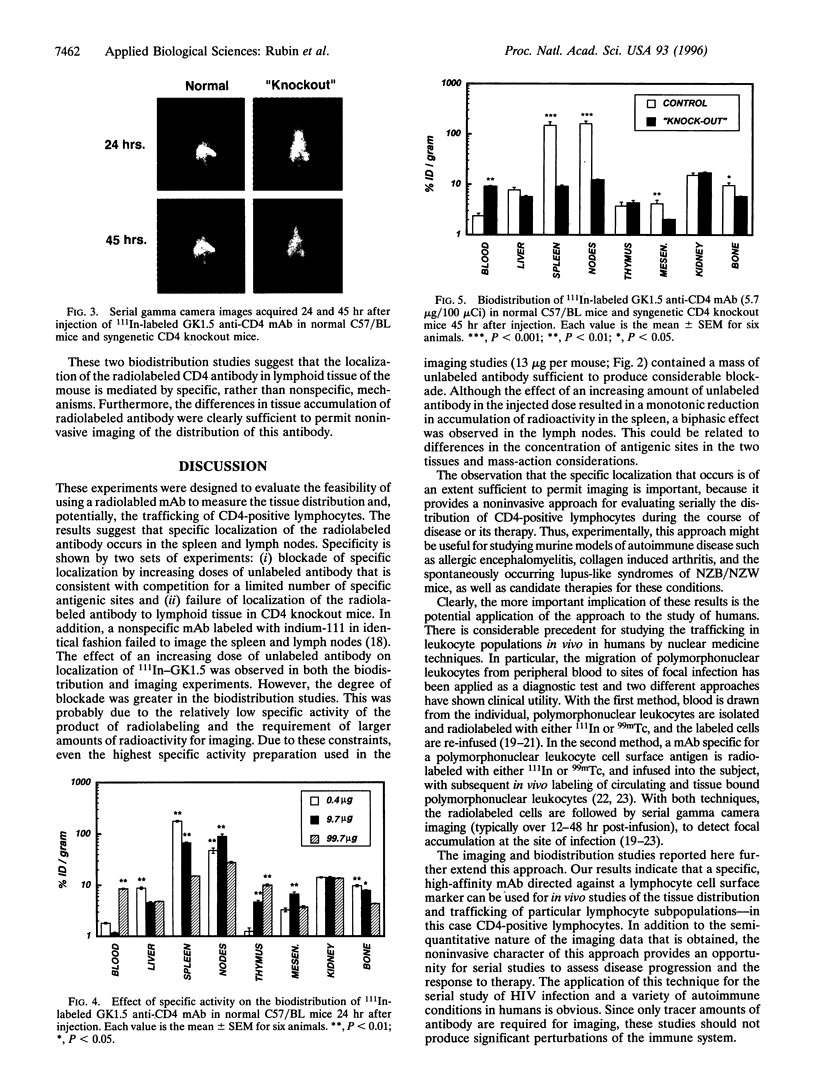
The tissue distribution of CD4 lymphocytes in normal C57/BL mice and CD4 knockout mice was determined by biodistribution measurements and gamma camera imaging with an 111In-labeled rat IgG2b monoclonal antibody directed against the murine CD-4 antigen. In normal mice high concentrations of antibody accumulated in the spleen and lymph nodes. At 45 hr after injection, the concentration of radiolabel in the spleen and lymph nodes of normal mice were 10- to 20-fold greater than in the corresponding tissue of the CD4 knockout mice and nonlymphoid tissues of both types of mice. At 24 and 45 hr, gamma camera images showed high concentrations of radiolabeled antibody in lymph node and spleen of normal but not knockout mice. These results indicate that radioimmunoscintigraphy with 111In-anti-CD4 is an excellent method for studying tissue distribution of CD lymphocytes in mice. Using an equivalent anti-human CD antibody, this method might be useful for studying the pathophysiology of conditions in which these cells play a critical role and for monitoring therapies for these disorders.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker W., Goldenberg D. M., Wolf F. The use of monoclonal antibodies and antibody fragments in the imaging of infectious lesions. Semin Nucl Med. 1994 Apr;24(2):142–153. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2998(05)80228-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Rutka J. T., Rosenblum M. L., McHugh T., Stites D. P., Levy J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus can productively infect cultured human glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodi F., Fuerstenberg S., Gidlund M., Asjö B., Fenyö E. M. Infection of brain-derived cells with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1244–1247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1244-1247.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi S., Lagakos S. W., Schooley R. T., Volberding P. A. CD4+ lymphocytes are an incomplete surrogate marker for clinical progression in persons with asymptomatic HIV infection taking zidovudine. Ann Intern Med. 1993 May 1;118(9):674–680. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-118-9-199305010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datz F. L. Indium-111-labeled leukocytes for the detection of infection: current status. Semin Nucl Med. 1994 Apr;24(2):92–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Quan Z. S., Wall K. A., Pierres A., Quintáns J., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Fitch F. W. Characterization of the murine T cell surface molecule, designated L3T4, identified by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: similarity of L3T4 to the human Leu-3/T4 molecule. J Immunol. 1983 Nov;131(5):2445–2451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Rota T. R., Hirsch M. S. Infection of monocyte/macrophages by human T lymphotropic virus type III. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1712–1715. doi: 10.1172/JCI112491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaw B. A., Mattis J. A., Melincoff G., Strauss H. W., Gold H. K., Haber E. Monoclonal antibody to cardiac myosin: imaging of experimental myocardial infarction. Hybridoma. 1984;3(1):11–23. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1984.3.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi Y., Miles S., Mitsuyasu R. T., Merrill J. E., Vinters H. V., Chen I. S. Dual infection of the central nervous system by AIDS viruses with distinct cellular tropisms. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.3646751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krejcarek G. E., Tucker K. L. Covalent attachment of chelating groups to macromolecules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jul 25;77(2):581–585. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locher J. T., Seybold K., Andres R. Y., Schubiger P. A., Mach J. P., Buchegger F. Imaging of inflammatory and infectious lesions after injection of radioiodinated monoclonal anti-granulocytes antibodies. Nucl Med Commun. 1986 Sep;7(9):659–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAfee J. G., Thakur M. L. Survey of radioactive agents for in vitro labeling of phagocytic leukocytes. I. Soluble agents. J Nucl Med. 1976 Jun;17(6):480–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElrath M. J., Pruett J. E., Cohn Z. A. Mononuclear phagocytes of blood and bone marrow: comparative roles as viral reservoirs in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):675–679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A. M. The utility of [99mTc]HMPAO-leukocytes for imaging infection. Semin Nucl Med. 1994 Apr;24(2):110–127. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2998(05)80226-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Gartner S. Isolation of HIV-1 from monocytes but not T lymphocytes. Lancet. 1987 Oct 17;2(8564):916–916. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. H., Young L. S., Hansen W. P., Nedelman M., Wilkinson R., Nelles M. J., Callahan R., Khaw B. A., Strauss H. W. Specific and nonspecific imaging of localized Fisher immunotype 1 Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection with radiolabeled monoclonal antibody. J Nucl Med. 1988 May;29(5):651–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Rose R. M., Groopman J. E., Markham P. D., Gallo R. C. Human T lymphotropic virus type III infection of human alveolar macrophages. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):281–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschachler E., Groh V., Popovic M., Mann D. L., Konrad K., Safai B., Eron L., diMarzo Veronese F., Wolff K., Stingl G. Epidermal Langerhans cells--a target for HTLV-III/LAV infection. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Feb;88(2):233–237. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12525402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]