Figure 2.
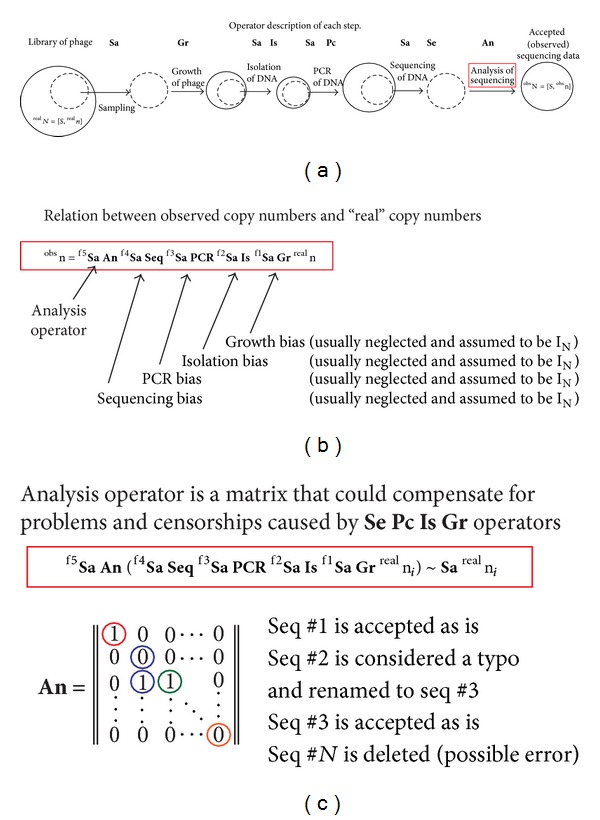
Operator description of the deep sequencing process. (a) A library of phage must be processed before deep sequencing. Each step involves sampling, which is either a deliberate partitioning of the sample or random loss of the sample. Each sample preparation state could (and does) introduce bias in sequence abundance. Each step, thus, is an operator chat changeing the n vector. (b) If we ignore bias during preparation, operators could be approximated as unity vectors, and sequencing could be represented as a product of sampling and analysis operators. (c) Analysis operator (A n) is a binary decision matrix, which describes what sequences are and are not considered as errors. Decisions, such as removal of sequences or correction of sequences, are the most important because they decide which “observed” sequences are considered “real.” To make the analysis of the selection process meaningful, the same A n operator should be used in all analyses.
