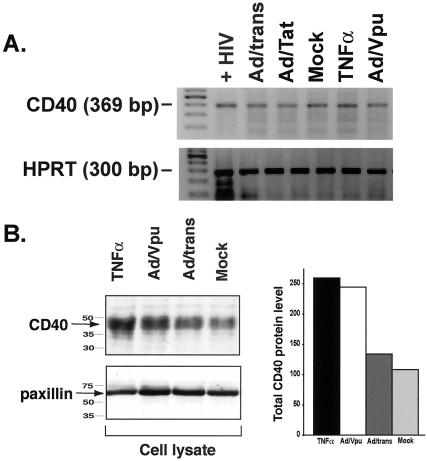
FIG. 5.
HIV-Vpu increases CD40 protein levels in endothelial cells via a posttranscriptional mechanism. (A) RT-PCR for CD40-specific transcripts reveals no induction of CD40 message in EC infected with Ad/Vpu (Ad/Vpu) relative to mock-infected EC (Mock), EC infected with Ad/trans alone (Ad/trans), or EC infected with Ad/Tat (Ad/Tat). A slight increase in CD40 RNA was observed in cytokine (TNF-α)-stimulated EC. EC infected with HIV (+HIV) were included as a positive control for CD40 amplification. Amplified PCR products at the expected molecular weights for CD40 (369 bp; top panel) and HPRT (300 bp; bottom panel) were visualized by ethidium bromide staining. Primer sequences and PCR conditions are described in Materials and Methods. (B) Total CD40 protein levels were determined by Western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates. The levels of the cellular protein paxillin in each lysate were measured as a loading control. CD40 levels in Ad/Vpu-infected cells (Ad/Vpu) were twice that seen in mock-infected (Mock) or Ad/trans-infected (Ad/trans) control cells and were comparable to levels induced by stimulation with TNF-α. CD40 levels were quantitatively measured by densitometry and are graphically represented. Both experiments represent cells at 48 h p.i. Similar results were detected at 24 h p.i.