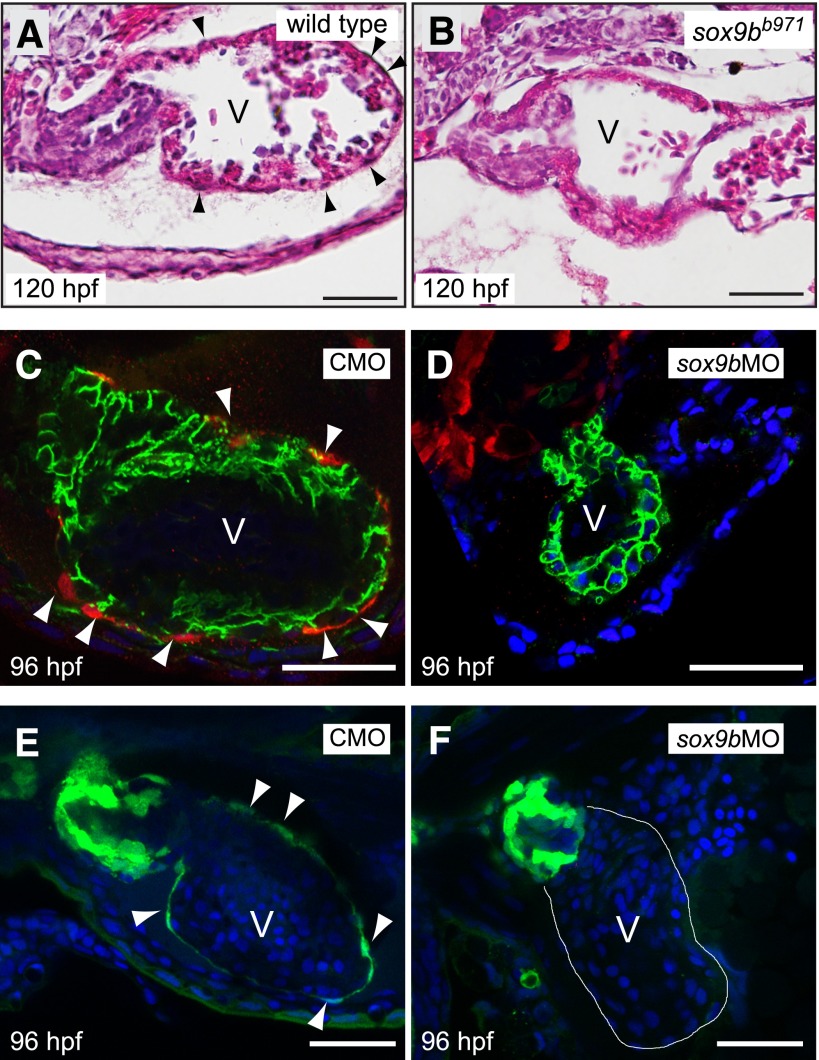
Fig. 5.
Sox9b is required for zebrafish epicardium development. (A and B) Brightfield images of hematoxylin and eosin–stained hearts from representative wild-type larva (A) and homozygous sox9bb971 null mutant larva (B) at 120 hpf. Black arrowheads indicate epicardial cells. (C and D) Embryos from the tcf21:DsRed epicardial cell reporter line were injected with the control (CMO) or sox9b MO (sox9bMO), and examined using confocal microscopy at 96 hpf for epicardium formation. Red indicates expression of tcf21, with white arrowheads indicating epicardial cells. Green indicates immunostaining for activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM), marking cell boundaries, and the blue is 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining, revealing nuclei. (E and F) Eggs from the pard3-GFP epicardial cell reporter line were injected with the control or sox9b MO, and examined using confocal microscopy at 96 hpf for epicardium formation. Green indicates expression of pard3 in epicardial cells which are indicated with white arrowheads. The blue is DAPI staining, revealing nuclei. For all panels representative images are shown with a minimum of n = 6 per group. Scale bar, 50 μm.