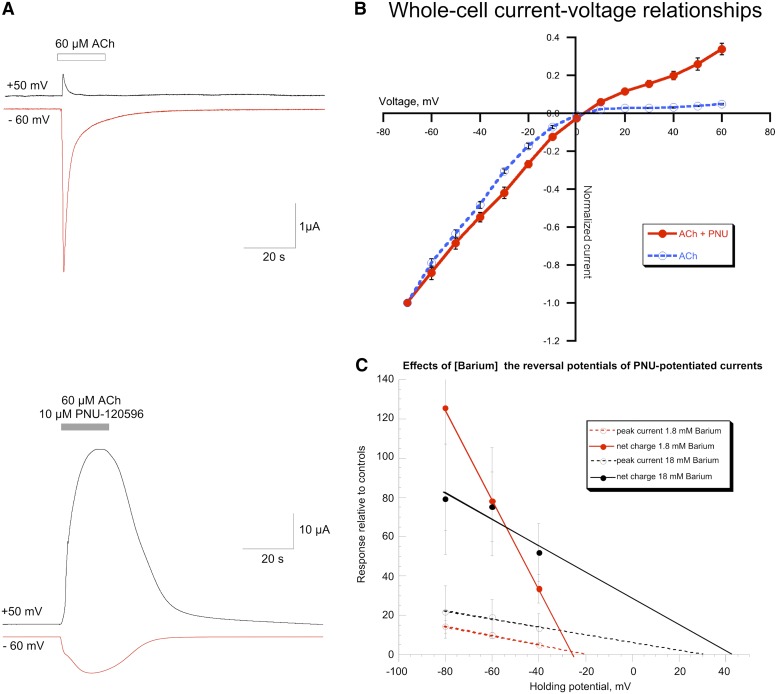
Fig. 8.
Effects of PNU-120596 on the current-voltage relationships of α7-mediated currents. (A) The upper traces illustrate the strong inward rectification of control α7 currents for receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. The net charge of responses measured at the depolarizing voltage (+50 mV) was a small fraction (3.4% ± 1.0%, n = 6) of that of responses recorded at the standard holding potential of −60 mV. In contrast, as shown in the lower traces, when measured relative to initial ACh controls, the absolute net charge of the responses evoked by 60 μM ACh plus 10 µM PNU-120596 at +50 mV was not smaller than those recorded at −60 mV. The potentiation factors determined from multiple cells were 286-fold ± 85-fold and 177-fold ± 36-fold larger than −60 mV controls for +50 and −60 mV responses, respectively (n = 4). These sample traces were obtained from different cells but were scaled to the ACh control response of the respective cells. (B) The current-voltage relationships of whole-cell responses of α7-expressing A7R3HC10 cells to the pressure application of 1 mM ACh alone (n = 5) or 100 µM ACh plus 10 µM PNU-120596 (n = 5). (C) Barium permeability of PNU-120596–potentiated α7 currents. Calcium-free Ringer’s solutions were made as previously described (Francis and Papke, 1996) with either 1.8 mM BaCl2 (and 48.6 mM sucrose) or 18 mM BaCl2. Cells were first tested for responses to control applications of 60 µM ACh alone in the low barium solution and then either kept in the low barium Ringer’s, or switched to the high barium solution for a series of stimulations with 30 µM ACh plus 6 µM PNU-120596 at different holding potentials. Current-voltage relationships were calculated by linear regression.