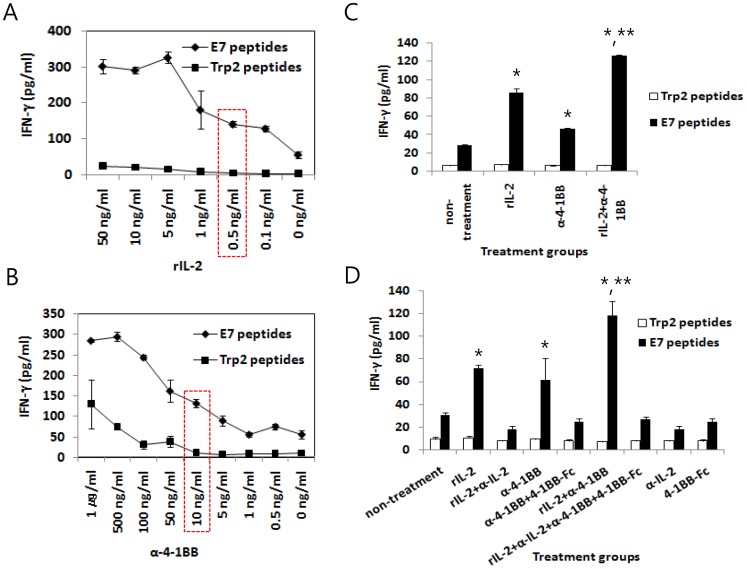
Figure 7. Increased production of IFN-γ from Ag-specific CD8+ T cells by treatment with IL-2 and anti-4-1BB Abs, and its blockade by treatment with anti-IL-2 Abs and 4-1BB-Fc.
Mice were immunized by IM-EP with 50 µg of E7 DNA vaccines (pE7) at 0 and 1 weeks. At 2 weeks, the mice were sacrificed and then the spleens were removed for immune cell isolation. The immune cells (6×106 cells/ml) were stimulated in vitro with either 1 µg/ml E7 CTL epitopes or control Trp2 peptides in the presence of an increasing dose of rIL-2 (A) and anti-4-1BB Abs (B) for 3 days. Red-dotted boxes denote the dose of rIL-2 and anti-4-1BB Abs that yields the half maximal IFN-γ production. (C) The immune cells were stimulated in vitro with either 1 µg/ml E7 CTL epitopes or control Trp2 peptides in the presence of rIL-2 (0.5 ng/ml) and anti-4-1BB Abs (10 ng/ml) for 3 days. (D) Similar experiments in Fig. 7C, except that cRPMI containing rIL-2 and anti-4-1BB Abs was reacted for 1 h 30 min with anti-IL-2 antibodies (50 ng/ml) and 4-1BB-Fc (1 µg/ml) prior to immune cell stimulation. The cell supernatants were used to detect IFN-γ. The values and bars represent the mean INF-γ and SD, respectively. This study was repeated twice with similar results. *p<0.05 using one-way ANOVA compared to non-treatment. **p<0.05 using one-way ANOVA compared to rIL-2 and anti-4-1BB.