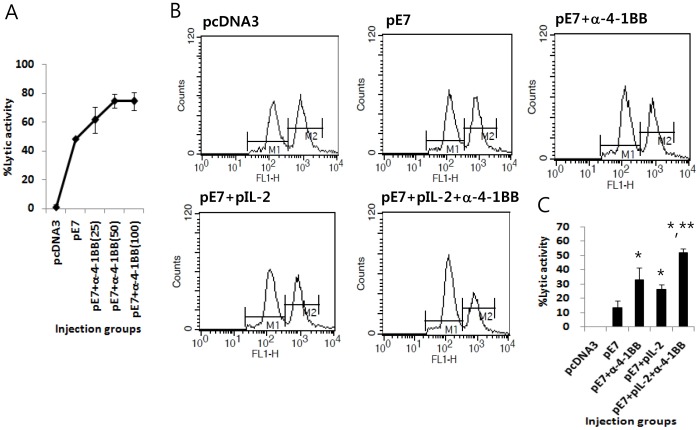
Figure 8. Increased Ag-specific CTL lytic activity in vivo by co-injection of E7 DNA vaccines with IL-2 cDNA and anti-4-1BB Abs.
(A) Each group of mice (n = 5) was immunized by IM-EP with 50 µg of E7 DNA vaccines (pE7) at 0 and 1 weeks. The animals were also injected i.p. with different doses of anti-4-1BB Abs (25, 50 and 100 µg per mouse) at 0 and 1 weeks. The animals were tested for in vivo CTL lytic activity at 2 weeks, as described in “Materials and Methods.” The mice were sacrificed after 10 h and the splenocytes were analyzed by FACS to measure the level of CFSE-labeled cells in each subset. (A) shows the mean % CTL lytic activity of each test group and SD. (B,C) Each group of mice (n = 5) was immunized by IM-EP with either pE7 (50 µg/mouse) or pE7 (50 µg/mouse)+IL-2 cDNA (10 µg/mouse) at 0 and 1 weeks. The animals were also injected i.p. with anti-4-1BB Abs (25 µg/mouse) at 0 and 1 weeks. The animals were tested for in vivo CTL lytic activity at 2 weeks, as described in “Materials and Methods.” The mice were sacrificed after 8 h and the splenocytes were analyzed by FACS to measure the level of CFSE-labeled cells in each subset. M1, un-pulsed CFSE low population; M2, E7-pulsed CFSE high population. (C) shows the mean % CTL lytic activity of each test group and SD. *p<0.05 using one-way ANOVA compared to pE7. **p<0.05 using one-way ANOVA compared to pE7+anti-4-1BB or pE7+pIL-2.