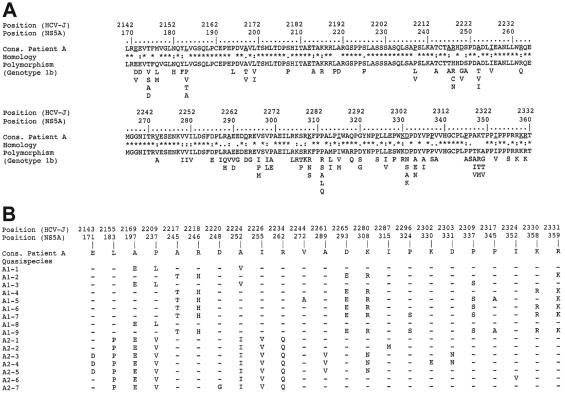
FIG. 2.
Natural variability of previously reported and patient A NS5A sequences in the transcriptional activation region. Amino acids are denoted by their single-letter code, and positions in the sequences are numbered according to both the HCV polyprotein and the NS5A protein in the prototype HCV genotype 1b HCV-J strain. (A) Polymorphism of previously reported NS5A sequences relative to patient A consensus sequence. “Cons.” represents the consensus amino acid sequence of patient A, derived from the alignment of this patient's 16 quasispecies variants with the CLUSTAL W program (45). Homology refers to the polymorphism observed in the 215 natural HCV genotype 1b NS5A variants recovered from EMBL and accessed through our database (HCVDB; http://hepatitis.ibcp.fr). Fully conserved, conserved, and similar residues at each position are symbolized by an asterisk, a colon, and a dot, respectively. The polymorphism of the 215 NS5A variants is presented as the repertoire of amino acids at each position, in decreasing order of observed frequency, from top to bottom (35). The least frequently observed residues (<1%) are not shown, because they could have been due to PCR and/or sequencing errors and/or sequencing of defective viruses. (B) Summary of patient A's quasispecies variant variability. Only the amino acid positions with one or several observed substitutions are shown. “Cons.” refers to patient A's consensus sequence. The sequences of the nine variants isolated at the start of follow-up are designated A1-i, where i varies from 1 to 9, while the seven sequences isolated at the end of follow-up are designated A2-j, where j varies from 1 to 7. Amino acids identical to those in the consensus sequence are represented by a hyphen.