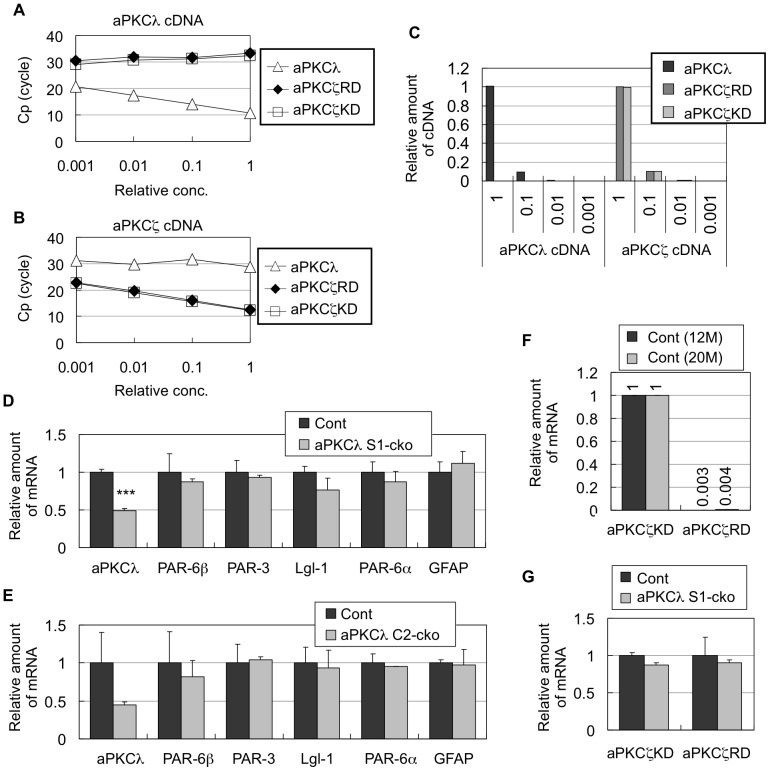
Figure 3. Quantitative RT-PCR of aPKCλ and its related genes in aPKCλ conditional deletion mice.
(A, B) Specificity of primer sets for aPKCλ and aPKCζ for quantitative PCR. Plasmid DNA for mouse aPKCλ cDNA (A) or aPKCζ cDNA (B) at indicated relative concentrations was subjected to real-time PCR using primers of aPKCλ and aPKCζ (RD or KD). Crossing point (Cp) means the cycle number of first detection of positive signal for PCR product. Low Cp indicates efficient detection of template cDNA, whereas high Cp without inverse correlation with the amount of the input indicates no significant detection. (C) Data in (A) and (B) were used for quantification of relative amounts of cDNA. Specific amplifications by each primer set were confirmed. (D, E) Quantitative RT-PCR of aPKCλ and indicated genes in cerebra of 11-month-old male mice harboring aPKCλ flox/flox (Cont) or aPKCλ flox/flox; S1-cre (aPKCλ S1-cko) (D, n = 3 for each), or 20-month-old male mice harboring aPKCλ flox/flox (Cont) or aPKCλ flox/flox; C2-cre (aPKCλ C2-cko) (E, n = 3 for each). Amounts relative to control are shown. (F) Quantitative RT-PCR of aPKCζ in cerebra of aPKCλ flox/flox (Cont) male mice at 11 months or 20 months of age (n = 3 for each). aPKCζ plasmid DNA was used as standard for quantification. Primer sets for aPKCζ RD and KD were used to detect full-length aPKCζ and both aPKCζ/PKMζ, respectively. The values obtained by aPKCζ KD primer set were taken as 1. (G) Quantitative RT-PCR of aPKCζ and PKMζ in cerebra of 11-month-old male mice harboring aPKCλ flox/flox (Cont) or aPKCλ flox/flox; S1-cre (aPKCλ S1-cko) (n = 3 for each). Amount relative to control is shown. Values are means ±SD.