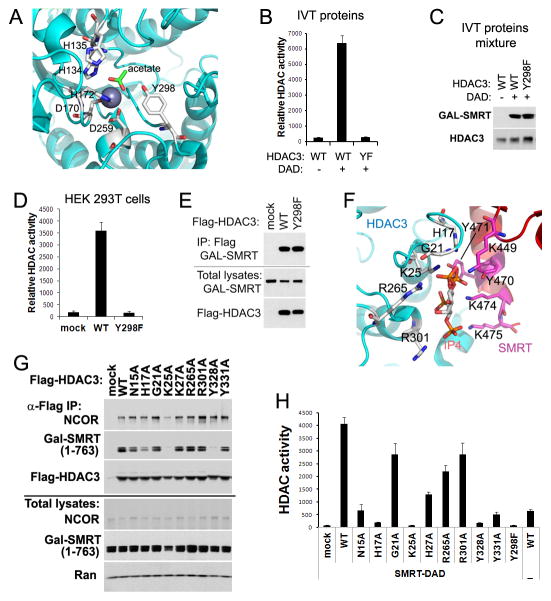
Figure 2. Mutations Y298F (YF) and K25A (KA) abolish HDAC3 enzymatic activity by distinct mechanisms.
(A) Key residues within the HDAC3 catalytic site. (B) In vitro-translated (IVT) HDAC3 wild-type (WT) or YF mutant were mixed with IVT GAL-tagged SMRT-DAD (amino acid 1–763), followed by HDAC enzyme assay. Values are fluorescence signal intensities. (C) Immunoblot analysis of the above IVT proteins mixtures. (D) Flag-tagged HDAC3 and GAL-tagged SMRT (1–763) were co-expressed in HEK 293T cells. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with Flag antibodies followed by HDAC assay. (E) Immunoblot analysis of the above immunoprecipitates (IP). (F) Potential residues involved in binding of HDAC3 with SMRT-DAD and inositol phosphates Ins(1,4,5,6)P4 (IP4). (G) Flag-HDAC3 mutants and SMRT (1–763) were co-expressed in HEK 293T cells. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with Flag antibodies followed by Immunoblot analysis. (H) HDAC assay of the above immunoprecipitates. All error bars, s.e.m. from triplicate assays. See also Figure S2.