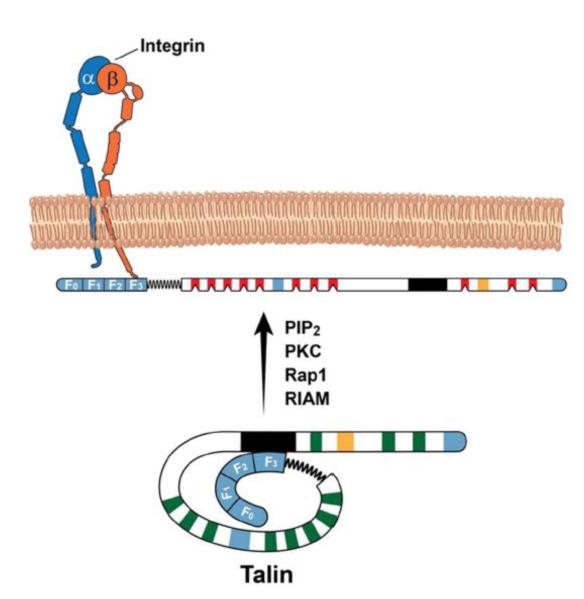
Fig 2. Structure of talin.
Talin can be subdivided into head (talin-H) and rod (talin-R) regions. Talin-H is comprised of F0, F1, F2 and F3 domains while the talin-R has ~11 vinculin- and 3 actin-binding sites (in blue). The vinculin binding sites are dormant (in green) and are likely mechanoactivated (in red). PIP2, PKC, Rap1 and or RIAM can relieve the autoinhibitory effect of talin-R (1654-2344aa; black region) on F3 domain, promoting talin binding to β CT. The secondary integrin binding site is in orange.