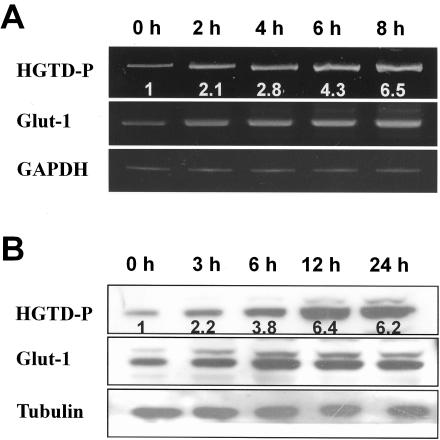
FIG. 1.
Hypoxia induces transcriptional and translational upregulation of HGTD-P. PC-3 cells in degassed medium were exposed to hypoxic conditions (0.5% O2) for the indicated periods. (A) cDNA was synthesized from total RNAs extracted from PC-3 cells exposed to hypoxia for the indicated time periods and subjected to reverse transcription-PCR analysis; 32, 30, and 26 cycles of amplification were performed for HGTD-P, Glut-1, and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), respectively. Mean increases in HGTD-P mRNA expression (HGTD-P/GAPDH) compared with that of normoxic cells are presented. (B) We subjected 30 μg of cell lysates extracted from hypoxia-exposed cells for the indicated time periods to Western blot analysis with polyclonal anti-HGTD-P (L16), anti-Glut-1, or antitubulin antibody. The mean increases in HGTD-P protein expression (HGTD-P/tubulin) compared with that of normoxic cells are presented.