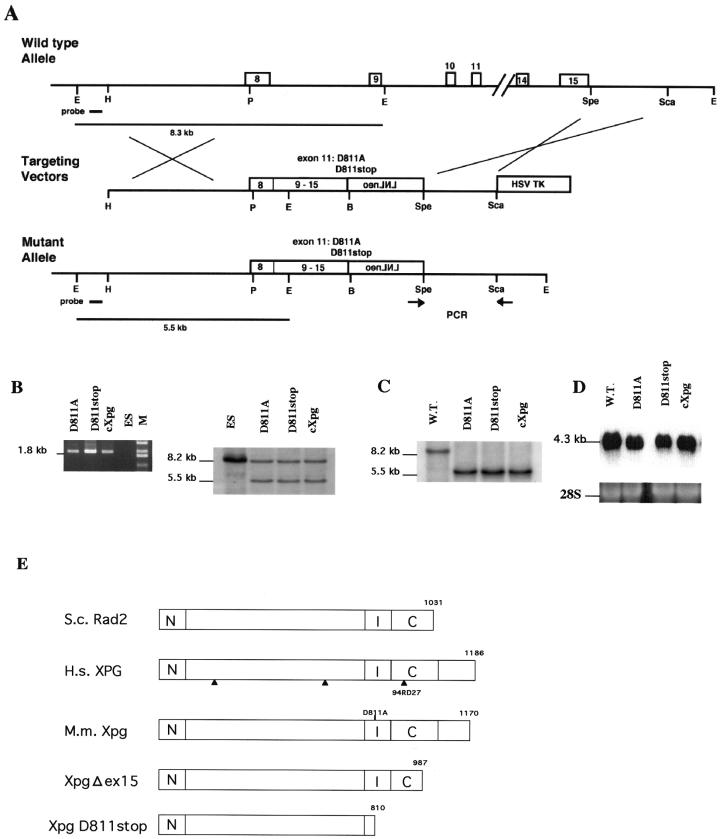
FIG. 2.
Generation of a truncation or base substitution mutation in the Xpg gene by the cDNA-mediated knock-in method. (A) Schematic of generation of mutations at the Xpg locus by the cDNA-mediated knock-in method. Exons 8 to 15 are shown. PCR primers are indicated by arrows. The 5′ probe used for Southern blot analysis is indicated by a solid bar on the wild-type map at the top of panel A, and the diagnostic fragments of 5.5 and 8.3 kb are indicated by solid lines at the bottom of panel A. Abbreviations: B, BamHI; E, EcoRI; H, HindIII; P, PstI. (B) PCR and Southern blot analyses of the targeted ES clones, ES-D811A, ES-D811stop, and ES-cXpg. The size of the predicted PCR product for mutant alleles was 1.8 kb, and no PCR product was amplified from the wild-type allele. Southern blot analysis with the 5′ probe also detected the predicted restriction fragments shown in panel A. Lanes: M, size markers; ES, ES cells used as a control. (C) Southern blot analyses of offspring from intercrosses between chimeric males and C57BL/6J females. +/+ represents the wild type (W.T.). cXpg/cXpg, D811A/D811A, and D811stop/D811stop represent homozygous cXpg, XpgD811A, and XpgD811stop mutants, respectively. (D) Northern blot analysis of total RNA from newborn mice, which were derived from heterozygous intercrosses and were determined to be homozygous mutants, with Xpg cDNA as the probe. As a loading control, the 28S rRNA band is shown. (E) Schematic of mutations in the Xpg protein. Arrows indicate the locations of mutations in XPG where the protein terminates in three XPG/CS patients. N and I indicate the highly conserved N-terminal and internal regions. C indicates the moderately conserved C-terminal region. The Xpg and S. cerevisiae (S.c.) Rad2 proteins have 45.5, 52.6, and 34.2% identical residues in the N, I, and C regions, respectively. In the XpgΔex15 and XpgD811stop mutant proteins, the last 183 and 360 amino acids were deleted, respectively. In the XpgD811A mutation, the highly conserved D811 residue of the Xpg protein was replaced with alanine. H.s., Homo sapiens; M.m., Mus musculus.