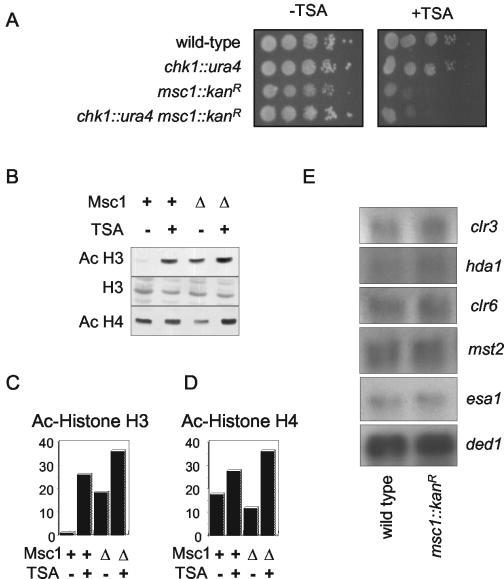
FIG. 5.
Deletion of msc1 affects cellular sensitivity to TSA and alters the state of histone acetylation in vivo. (A) An msc1::kanR deletion strain is TSA sensitive. Tenfold serial dilutions of the indicated strains were spotted on rich medium (−TSA) or rich medium containing 25 μg of TSA/ml (+TSA) and incubated at 30°C for 3 days. (B) Deletion of Msc1 results in hyperacetylation of histone H3. Histones were isolated from wild-type cells (Msc1 +) or an msc1::kanR deletion strain (Msc1 Δ). Histones (25 μg) were loaded on a 15% polyacrylamide gel and transferred to nylon membrane. Acetylated (Ac) histones were detected using antibody that recognizes histone H3 diacetylated on lysines 9 and 14 (upper panel), total histone H3 (middle panel), or histone H4 tetra-acetylated on lysines 5, 8, 12, and 16 (lower panel). (C and D) The data presented in panel B was quantitated using ImageQuant software normalized with histone H3 values and plotted to convey the relative amounts of acetylation in the different strains. (E) Northern blot analysis of genes affecting histone acetylation. RNA was isolated from wild-type and msc1::kanR cells and probed for the expression level of the indicated genes. The clr3, hda1, and clr6 genes encode HDAC. The mst2 and esa1 genes encode putative HAT, as suggested by sequence similarity to genes in other organisms. The ded1 gene, encoding a DEAD-box helicase involved in translation initiation, was used as a loading control.