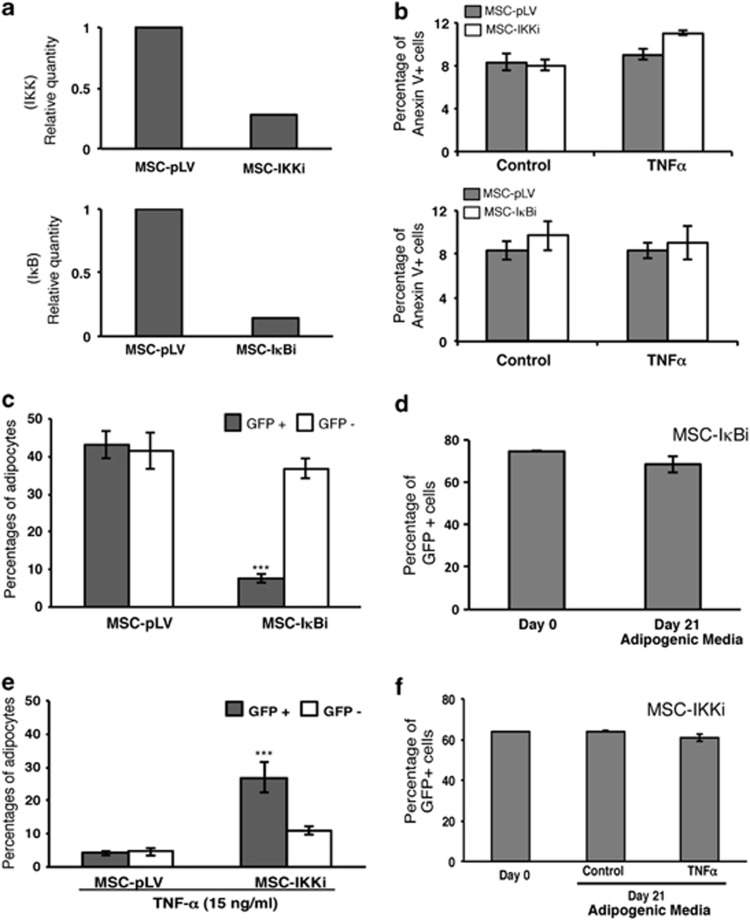
Figure 2.
NF-κB is important for TNFα induced inhibition of adipogenesis in MSCs. (a) IKKβ and IκBα expression levels by real-time qPCR in transduced cells. IKK and IκBα transcripts were ‘knocked down' by specific shRNA with more than 80% efficiency. Relative transcript expression levels were normalized to IKKβ and IκBα transcript expression levels from pLV-empty vector infected MSCs, respectively. (b) Analysis of apoptotic cells in IKKβ (upper panel) and IκBα knockdown cells in the presence/absence of TNFα. The percentage of apoptotic cells (Annexin V positive) was measured at 6-days post-infection by flow cytometry. Results show the means±S.D. of triplicate samples. (c) IκBα knockdown inhibits adipogenesis capacity in MSCs, which is consistent with the phenotype observed in the presence of TNFα, ***P<0.001. (d) Percentage of GFP expression in IκBα transduced cells before (Day 0) and after (Day 21) adipogenesis differentiation period was analyzed by flow cytometry. (e) IKKβ knockdown rescues adipogenesis from the inhibition causes by TNFα. ***P<0.001. (f) Percentage of GFP expression in IKKβ-transduced cells before (Day 0) and after (Day 21) adipogenesis differentiation period in the presence/absence of 15 ng/ml of TNFα was analyzed by flow cytometry). Results show the means±S.D. of triplicate samples