FIG. 3.
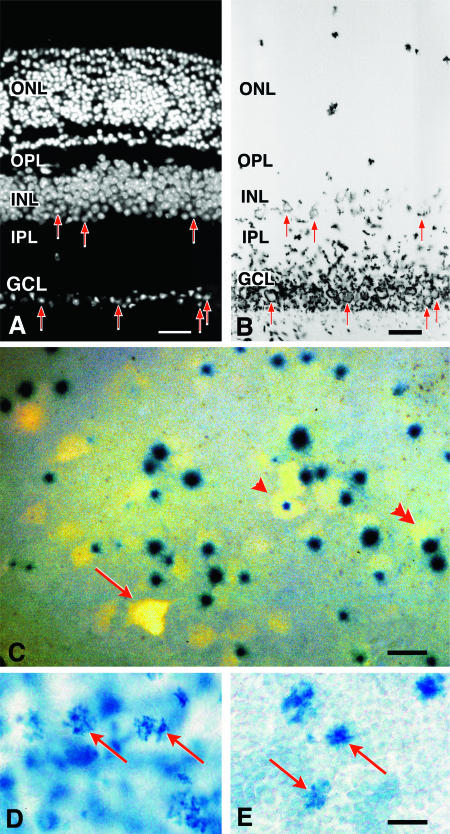
β-Galactosidase is primarily expressed in retinal ganglion cells and in a subset of cells in the inner nuclear layer. (A and B) Histological analysis of BluoGal-stained retinas from R3/+ mice. (A) Fluorescent image of a transverse section through a mouse retina (stained with DAPI to highlight nuclei); (B) bright-field image of the same section. BluoGal staining is localized around cells in the ganglion cell layer (GCL). Stain is also deposited in the inner plexiform layer (IPL), which contains the majority of ganglion cell dendritic processes. Some cells in the inner region of the inner nuclear layer (INL) are also labeled. Examples of labeled cells in both the GCL and INL are highlighted with arrows in both panels. No staining is evident in the photoreceptors of the outer nuclear layer (ONL). OPL, outer plexiform layer. Bar, 25 μm. (C) Photomicrograph (taken with both fluorescent and bright-field illumination) of a flat-mounted retina from a R3/+ mouse, showing colocalization of Fluorogold and βGeo activity (as revealed by X-Gal staining) in cells of the ganglion cell layer. Fluorogold labeled the cytoplasm, while X-Gal concentrated in the nucleus. Some ganglion cells have central nuclei (arrowhead), while most cells have nuclei positioned eccentrically (double arrowhead). In the ganglion cell layer, 91% ± 1% of Fluorogold-labeled cells (n = 584) express βGeo. Incomplete penetration of the X-Gal stain could account for the small percentage of Fluorogold-labeled cells that are not associated with βGeo expression (arrow); alternatively, these cells may represent a subset of retinal ganglion cells that do not express the transgene. Bar, 10 μm. (D and E) Bright-field images of whole-mounted retinas stained with BluoGal. The focal plane is centered on the inner nuclear layer of each retina, showing scattered labeled cells (arrows). The control retina has an extensive blue background due tolabeled ganglion cells (D). A retina taken from the contralateral eye of the same mouse 2 weeks after optic nerve crushing shows reduced staining of the ganglion cell layer but no change in labeling in the inner nuclear layer (E). Bar, 5 μm.