FIG. 1.
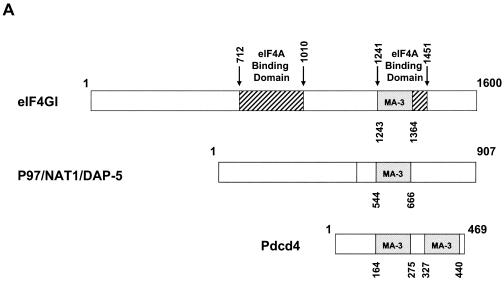
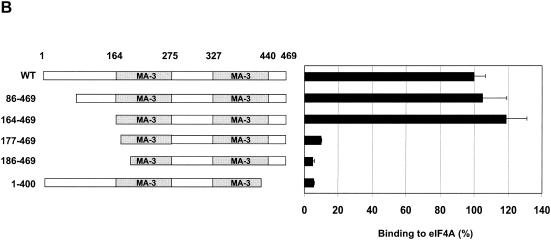
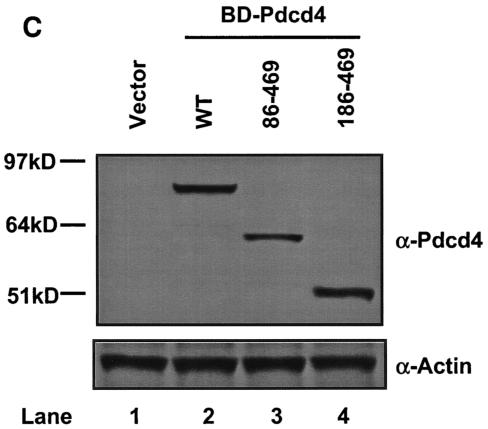
Both MA-3 domains of Pdcd4 are required for eIF4A-binding activity. (A) Structures of eIF4G1, DAP-5/NAT1/p97, and Pdcd4. The numbers refer to the size (in amino acids) of eIF4G1, DAP-5/NAT1/p97, and Pdcd4 and to the location of the eIF4A-binding domain and the MA-3 domain (2, 17, 24). The MA-3 domains (gray box) in eIF4G1, DAP-5/NAT1/p97, and Pdcd4 are indicated schematically. The eIF4A-binding domains (strip box and arrows) in eIF4G1 are indicated schematically. (B) Partial deletion of N- or C-terminal MA-3 domain of Pdcd4 dramatically decreases the eIF4A-binding activity. Plasmid pCMV-BD-Pdcd4 (50 ng) (wild type [WT] or deletion mutants) was transiently transfected with pCMV-AD-eIF4A (50 ng) and Gal4-luciferase reporter DNA (25 ng) into JB6 RT101 cells. After 48 h, cells were lysed and the luciferase activity was measured. The luciferase activity with wild-type Pdcd4 was designated as 100%. These experiments were repeated three times with five independent transfections, and representative data are shown. The results are expressed as the means plus the standard deviation. (C) Protein expression level of wild-type and truncated Gal4 DNA-binding domain-Pdcd4. Cell lysates (15 μg) from transiently transfected empty vector (lane 1), wild-type (WT) Pdcd4 (lane 2), or truncated Pdcd4 (lanes 3 and 4) were separated on 10% Bis-Tris NuPage gels, transferred to nitrocellulose, and subjected to immunoblotting with Pdcd4 or actin antibody with visualization by chemiluminescent detection.