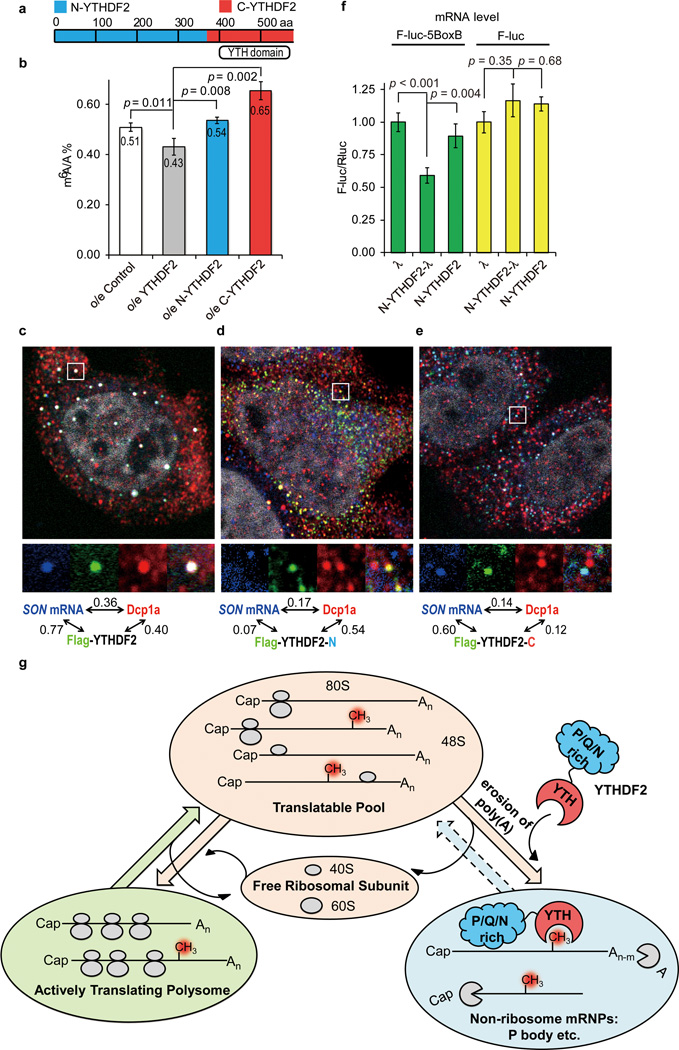
Figure 3. YTHDF2 affects SON mRNA localization in processing body (P-body).
a, Schematic of the domain architecture (aa stands for amino acids) of YTHDF2, N-terminal of YTHDF2 (N-YTHDF2, aa 1–389, blue) and C-terminal of YTHDF2 (C-YTHDF2, aa 390-end, red). b, Over-expression of full-length YTHDF2 led to reduced levels of m6A after 24 h, while over-expression of N-YTHDF2 or C-YTHDF2 increased the m6A/A ratio of the total mRNA. P values were determined using two-sided Student’s t-test for paired samples. Error bars, mean ± s.t.d., n = 4 (two biological replicates × two technical replicates). c–e, Fluorescence in situ hybridization of SON mRNA and fluorescence immunostaining of DCP1a (P-body marker), flag-tagged YTHDF2 (c), flag-tagged C-YTHDF2, (d) and flag-tagged N-YTHDF2 (e). Full-length YTHDF2 and C-YTHDF2 co-localize with SON mRNA (bearing m6A) while the full-length YTHDF2 significantly increases the P-body localization of SON mRNA compared to N-YTHDF2 and C-YTDF2. The numbers shown above figures are Pearson correlation coefficients of each channel pair with the scale of the magnified region (white frame) set as 2 µm × 2 µm. f, Tethering N-YTHDF2-λ to a mRNA reporter F-luc-5BoxB led to a ~40% reduction of the reporter mRNA level compared to tethering N-YTHDF2 or λ alone (green) and controls without BoxB (F-luc, yellow). P values were determined using two-sided Student’s t-test for paired samples. Error bars, mean ± s.t.d., n = 6 (F-luc-5BoxB) or 3 (F-luc). g, A proposed model of m6A-dependent mRNA degradation mediated through YTHDF2. The three states of mRNAs in cytoplasm are defined by their engagement with ribosome using the sedimentation coefficient range in sucrose gradient: >80S for actively translating polysome; 40–80S for translatable pool; 20–35S for non-ribosome mRNPs.