Figure 2.
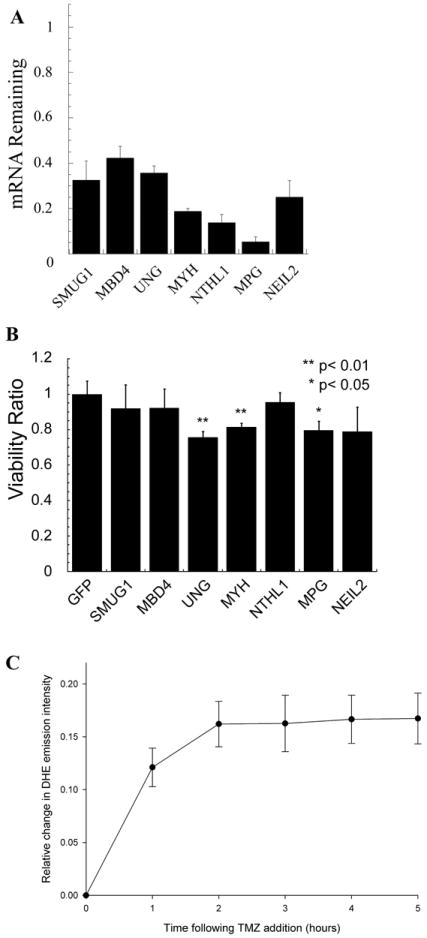
Glioma cells with shRNA knockdown of DNA glycosylases are more sensitive to the clinical alkylator TMZ. (A) Quantification of DNA glycosylase mRNA knockdown in cells as determined by qRT-PCR. TaqMan probes were used to quantify mRNA levels on an Applied Biosystems StepOnePlus machine. The qRT-PCR data were analyzed using the ΔΔCt method and was normalized to GFP infected plate controls. Gene expression of each gene was normalized to the expression of human ß-actin. The mean of three independent experiments is plotted ± SEM. (B) Validation of TMZ sensitization with knockdown of specific DNA glycosylases. T98G DNA glycoylase knockdown cell line sensitivity to TMZ was determined by an MTS assay 48 h after exposure to 1 mM TMZ. The viability ratio is double normalized to account for both vehicle treated shRNA mediated growth defects and toxicity of control cells to TMZ. The mean viability ratio of three independent experiments is plotted ± SEM. (C) TMZ treatment results in a time-dependent increase in reactive oxygen species as measured with the superoxide indicator dihydroethidium. Data were collected in 2-12 cells per stage position, with 15 stage positions in each of two separate experiments, as detailed in the methods section and as in Figure 3. There was a 12.1 +/- 1.8% increase in DHE emission intensity in the first hour which stabilized at 16.3 +/- 2.1% by 2 hours.
