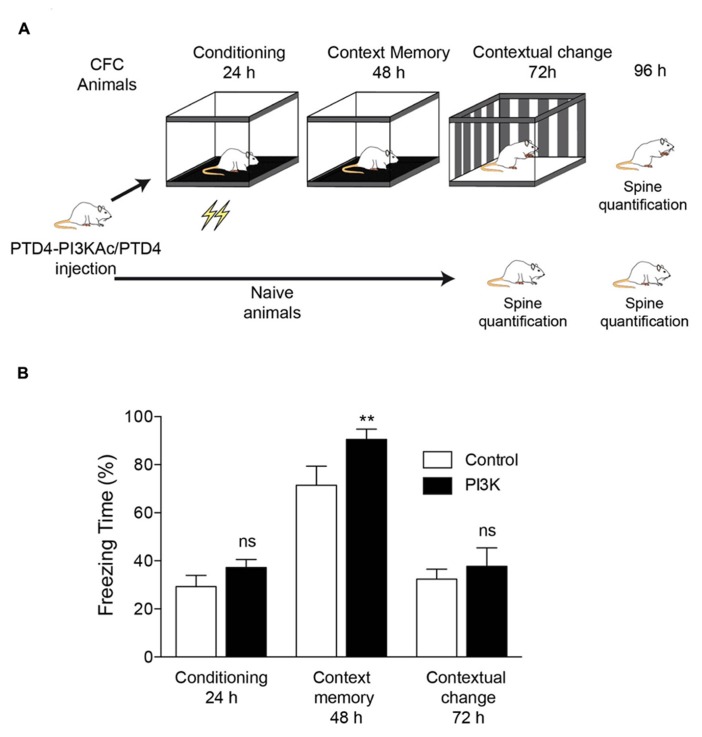
FIGURE 1.
PI3K activation improves a hippocampal-dependent learning behavior. (A) Illustration depicting the experimental design. All animals were subjected to the same handling treatment before the experiments. At time 0, they were injected either PTD4-PI3KAc or PTD4 as control. The experimental group was subjected to the CFC test (CFC animals), whereas the control group (naive animals) remained in their cages throughout the entire experiment. (B) CFC test results for animals injected with either PTD4-PI3KAc (black bars, n = 10) or the PTD4 control transduction domain (open bars, n = 10). No differences in freezing were observed during conditioning (24 h), indicating normal fear acquisition and no differences in sensitivity to the shocks. In the context memory test (48 h), PTD4-PI3KAc injected rats showed higher freezing levels than control rats when re-exposed to the conditioning chambers with no shock delivery. A contextual change to discard unspecific effects (72 h) showed no differences among animals, indicating that the memory effects are context-dependent (Student’s t-test). Animals were sacrificed 24 h later, i.e., 96 h after peptide injection.