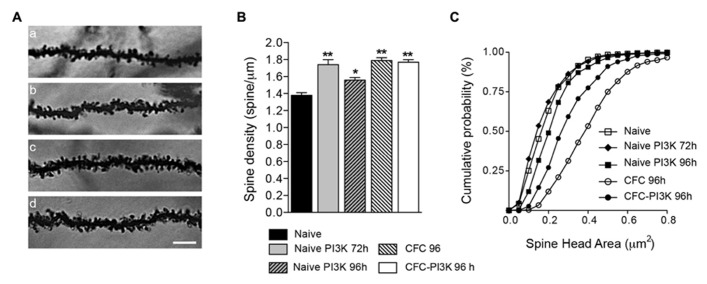
FIGURE 2.
PI3K activation and CFC modified spine density and head area. (A) Representative images (96 h after injection) of stratum oriens dendrites in the CA1 region of the hippocampus from Naive (a), Naive injected with PTD4-PI3KAc (b), CFC (c), and CFC injected with PTD4-PI3KAc (d) animals. Scale bar = 5 μm. (B) Mean average graph of spine density changes during: naive conditions (1.38 ± 0.03 spines/μm), after 72 and 96 h of PI3K activation (1.74 ± 0.06 and 1.56 ± 0.03 spines/μm, respectively) and after the CFC test (CFC-96 h; 1.79 ± 0.02 spines/μm and CFC-PI3K-96 h: 1.77 ± 0.03 spines/μm) (Student‘s t-test). (C) Cumulative frequency distribution of spine head areas under the experimental conditions. In naive animals, no effect was seen after 72 h, but a significant increased in spine head area was found 96 h after PI3K activation (Kolmogorov–Smirnov, p < 0.001), whereas CFC alone induced an even more pronounced shift toward large spine areas. Interestingly, in CFC tested animals, PI3K overactivation reduced spine head areas as compared to the CFC controls (Kolmogorov–Smirnov, p < 0.001).