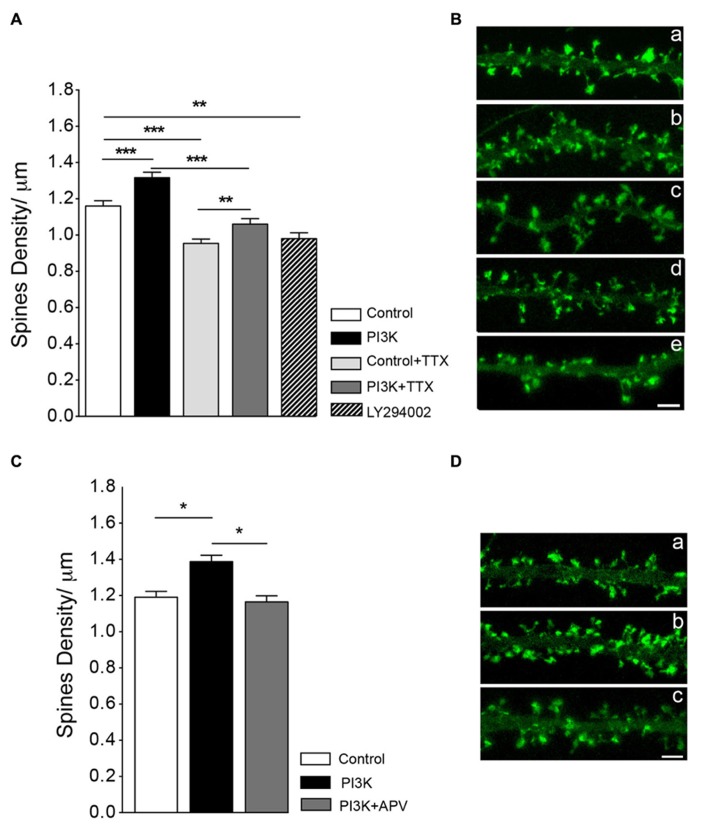
FIGURE 5.
Synaptic activity does not modulate spine formation in culture. (A) Neuronal activity is not required for PI3K-induced spine density increase. Spine density was quantified in cultures with and without PTD4-PI3KAc under normal conditions (control versus PI3K) and in cultures treated with TTX (2 μM) for 48 h (control + TTX versus PI3K-TTX). Compared to the control cultures, PTD4-PI3KAc significantly increased spine density regardless neuronal activity (from 1.16 ± 0.03 to 1.32 ± 0.03 spines/μm without TTX and from 0.95 ± 0.02 to 1.06 ± 0.03 spines/μm with TTX). (Student’s t-test). Treatment with a PI3K inhibitor activity for 48 h, reduces spine density a 15% (0.9 ± 0.03 spines/μm). (B) Representative dendritic segments of actin-GFP transfected neurons after 21DIV in control (a), PTD4-PI3KAc-treated (b), TTX-treated (c), TTX + PTD4-PI3KAc-treated (d) and LY294002-treated cultures (e). Scale bar = 2.5 μm. The number of dendrites analyzed in the different cultures was: 95 for Control, 91 for PI3K, 109 for control + TTX, 113 for PI3K + TTX and 137 for LY294002. (C) NMDAR receptor activation appears to be necessary for the formation of PI3K-induced spines. As before, spine density in response to PI3K activation was quantified in sister cultures under normal conditions (control versus PI3K) and in the presence of the NMDA receptor inhibitor d-APV (PI3K + APV). Spine density was significantly higher in PI3K as compared to the control culture (1.39 ± 0.04 versus 1.19 ± 0.03 spines/μm, respectively), whereas in the PI3K + APV culture, spine density was reduced back to control levels (1.16 ± 0.03 spines/μm) (Student’s t-test). (D) Representative dendritic segments from control (a), PI3K (b) and PI3K + APV (c) cultures. Scale bar = 2.5 μm. A total of 79 control; 73 PTD4-PI3KAc and 73 PTD4-PI3Kac+d-APV dendrites from four different cultures were analyzed.