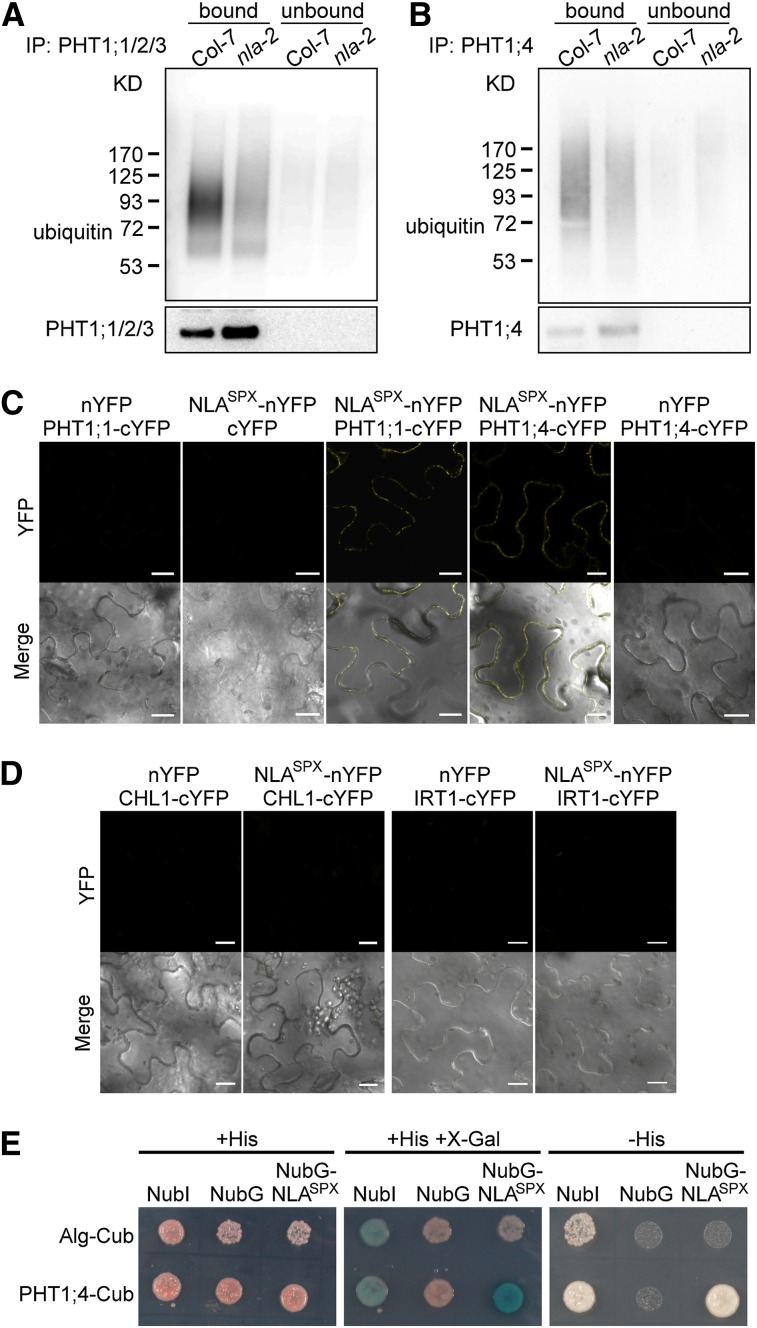
Figure 5.
PHT1;1 and PHT1;4 Are the Ubiquitination Substrates of NLA.
(A) and (B) In vivo ubiquitination of PHT1;1/2/3 (A) and PHT1;4 (B) in the roots of the wild type and nla-2 mutants under Pi-sufficient conditions and after 1 d of Pi recovery, respectively. The corresponding antibodies were used for immunoprecipitation (IP) (bound). Immunoprecipitation without adding antibodies (unbound) was used as negative control. PHT1;1/2/3 and PHT1;4 protein levels of the immunoprecipitation products are shown in the bottom panels. Col, Columbia.
(C) and (D) BiFC analysis of the interaction between NLASPX and PHT1;1 or PHT1;4 (C) and NLASPX and CHL1 or IRT1 (D). Reconstituted fluorescence signals were detected in the PM of tobacco leaf cells when NLASPX-nYFP was coexpressed with PHT1;1- or PHT1;4-cYFP but not with CHL1-cYFP or IRT1-cYFP. Coexpression of nYFP or cYFP with the corresponding PHT1;1-cYFP or PHT1;4-cYFP or NLASPX-nYFP constructs was used as an additional control. The top panels are YFP images, and the bottom panels are overlaid images of YFP and bright field. Bars = 20 μm.
(E) The interaction between NLASPX and PHT1;4 by split-ubiquitin yeast two-hybrid analysis. NubI and NubG, the wild type and mutated N-terminal fragment of ubiquitin with isoleucine and glycine at position 13, respectively; Cub, C-terminal ubiquitin. Dolichyl-phosphate beta-glucosyltransferase (Alg)-Cub is the control that could interact with NubI but not with NubG and NubG-NLASPX.