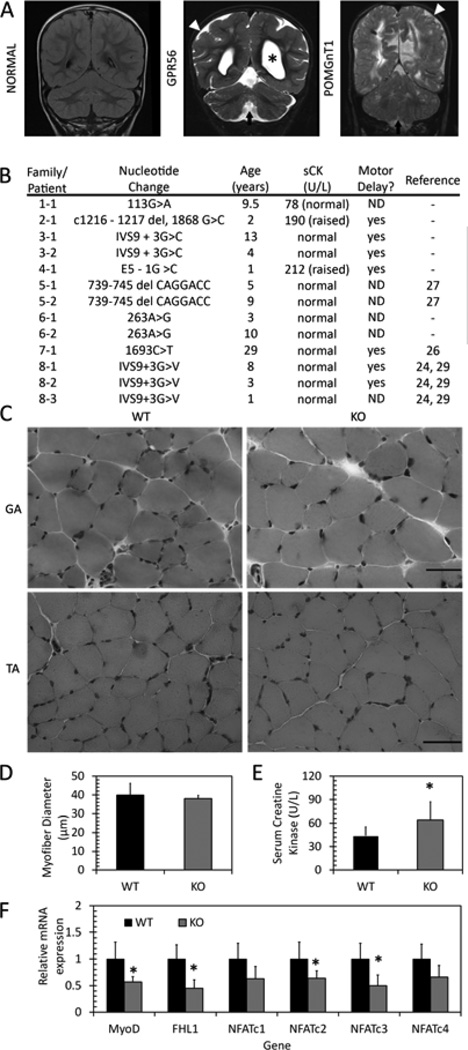
Figure 4. Muscle phenotypes in BFPP patients and GPR56 knockout mice.
A. Representative coronal flair MRI image from an unaffected individual (NORMAL) and coronal T2 images from individuals with confirmed mutations in GPR56 and POMGnT1. Patients exhibit enlarged ventricles (asterisks), presence of diffused cortical abnormalities (white arrowhead) and presence of cerebellar abnormalities, including a small vermis in the GPR56 patient (arrow). B. Serum creatine kinase levels and motor developmental delays in patients with BFPP. ND: Not determined. C. H&E staining of one-month-old gastrocnemius (top, GA) and tibialis anterior (bottom, TA) muscles shows no difference between wildtype and knockout muscle. Scale bars = 50 µm. D. Myofiber diameter in TA muscle shows no difference between WT and KO. E. Serum CK levels in WT and KO mice shows slightly elevated serum CK levels in knockout mice. *p=0.012, n = 11–12. F. mRNA expression in WT and KO gastrocnemius muscle. Expression of MyoD, FHL1, NFATc2, and NFATc3 are decreased in KO muscle. * p<0.05, n = 6.