Table 1.
Optimization of the oxa-Pictet-Spengler reaction.a
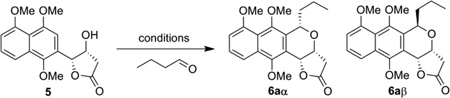 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | Lewis acids |
solvent | temp (ºC) |
conversion (%)b |
dr (6aα/6aβ)c |
| 1 | BF3·OEt2 | CH2Cl2 | 0-rt | 80(75) | 66:34 |
| 2 | Yb(OTf)3 | CH2Cl2 | 0-rt | 10 | 80:20 |
| 3 | Y(OTf)3 | CH2Cl2 | 0-rt | 23 | 67:33 |
| 4d | TiCl4 | CH2Cl2 | −78-rt | 70 | 70:30 |
| 5 | SnCl4 | CH2Cl2 | 0-rt | 100 | 60:40 |
| 6 | FeCl3 | CH2Cl2 | 0-rt | 100 | 52:48 |
| 7 | Cu(OTf)2 | CH2Cl2 | 0-rt | 85 | 89:11 |
| 8e | Cu(OTf)2 | CH2Cl2 | 0-rt | 95(90) | 91:9 |
| 9 | Cu(OTf)2 | DCE | 0-rt | (64) | 90:10 |
| 10 | Cu(OTf)2 | CHCl3 | 0-rt | (43) | 94:6 |
| 11f | Cu(OTf)2 | CH2Cl2 | 0-rt | (32) | 93:7 |
| 12g | Cu(OTf)2 | CH2Cl2 | 0-rt | (48) | 91:9 |
| 13 | FeCl3 | THF | 0-rt | (50) | 34:66 |
Reaction was performed with 0.2 mmol 5, 0.4 mmol aldehyde, and 50 mol % Lewis acid at 0 ºC. The temperature was allowed to subseqeuntly raise to rt over 4 h with stirring.
Conversion was determined by HPLC analysis. The data in the parentheses are the isolated yields after column chromatography.
dr ratio was determined by the proton NMR of crude products.
2 h reaction time.
Overnight.
Using 1,1-dimethoxybutane instead of butaldehyde.
Using 20 mol % Lewis acid.
