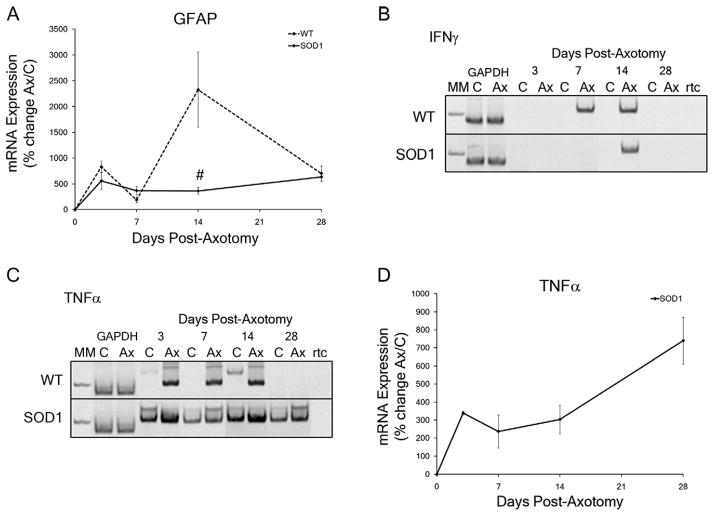
Figure 5.
Neuropil-specific mRNA expression levels in wild-type (WT) and presymptomatic SOD1 facial motor nuclei in response to facial nerve axotomy. A: Average percent of mRNA expression ± SEM in the axotomized facial nuclei relative to the uninjured control nuclei in WT and SOD1 mice. Time-course of mRNA expression includes no injury (0), 3, 7, 14, and 28 days post axotomy for GFAP. B,C: Electrophoresis of RT-PCR products from control and axotomized WT and SOD1 facial nuclei at 3, 7, 14, and 28 days post axotomy for IFNγ (B; 111 base-pair amplicon) and TNFα (C; 102 base-pair amplicon), along with the molecular weight marker (MM) 100 base-pair band, the internal standard (GAPDH), and a no reverse-transcriptase control (rtc). D: Average percent of mRNA expression ± SEM in the axotomized SOD1 facial nuclei relative to the uninjured control nuclei. Time-course of mRNA expression includes no injury (0), 3, 7, 14, and 28 days post axotomy for TNFα. Two-way ANOVA (group × time, for each gene individually) with Student-Newman-Keuls multiple comparison post hoc test: # represents a significant difference compared with WT, at P < 0.05.