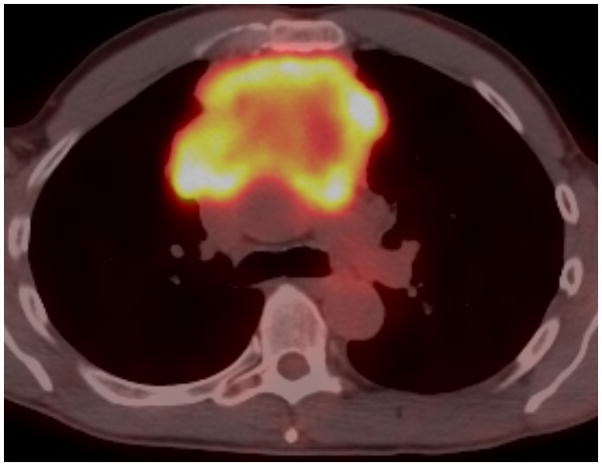
FIGURE 1.
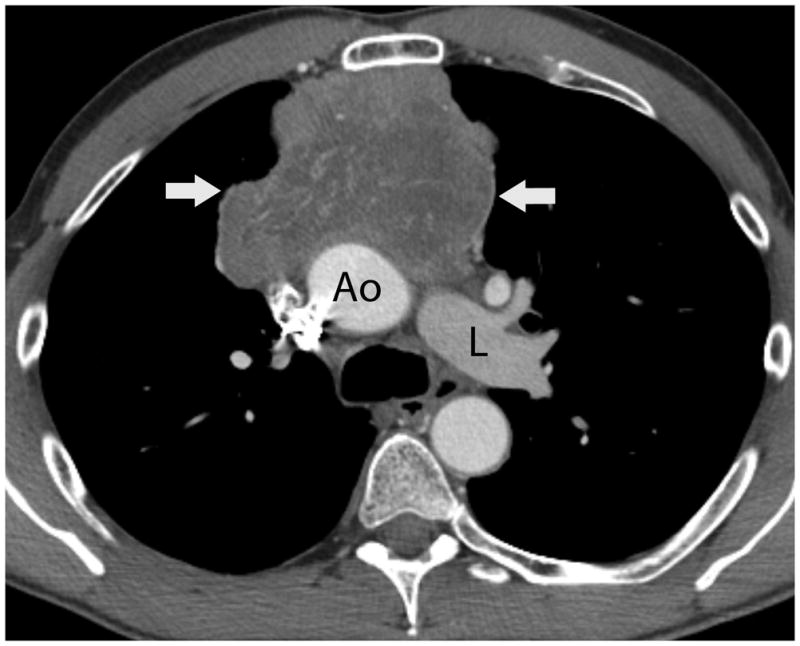
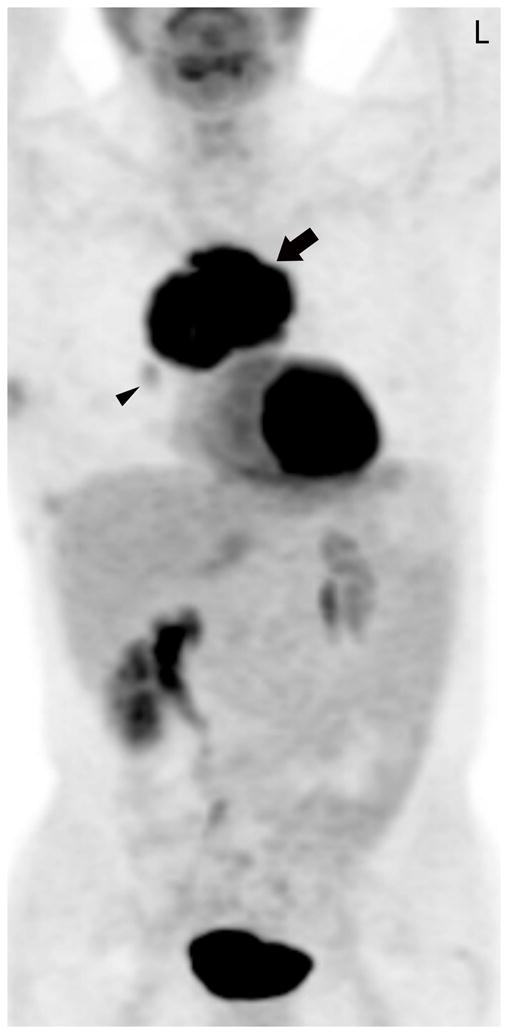
Fifty-four-year-old man with thymic carcinoma. Axial contrast-enhanced CT (A) at the level of the left pulmonary artery (L) demonstrated a large heterogeneous anterior mediastinal mass (arrows) surrounding 180° of the circumference of the ascending aorta (Ao). The coronal maximum intensity projection FDG PET image (B) and fused PET-CT image (C) show intense FDG uptake within the mass, with an SUVmax of 14.1 (arrow). Note mild FDG uptake in a right hilar lymph node (arrowhead), which biopsy proved to represent a lymph node metastasis, yielding a diagnosis of stage IVb disease. CT, computed tomography. FDG, fluorodeoxyglucose. PET, positron emission tomography. SUV, standardized uptake value.