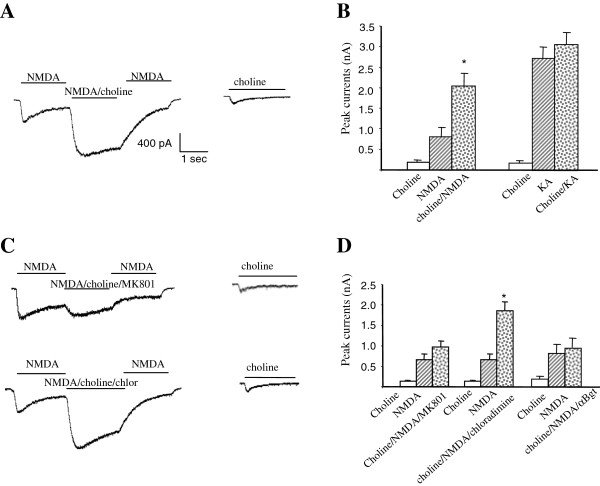
Figure 1.
Choline induced synergistic effect on NMDAR currents through the α 7-nAchR/NMDAR direct protein-protein interaction. (A) Co-application of 1 mM choline with 50 µM NMDA/10 µM glycine produced a synergistic effect that display a significantly larger current compared to the current induced by NMDA/Glycine alone (n = 43 of 47 cells, P < 0.01). (B) The choline induced synergistic effect is specific to NMDAR-mediated currents since no such an effect was detected on currents induced by 100 µM kainic acid. (C, D) The choline-induced synergistic effect is significantly inhibited by simultaneous application NMDAR channel blocker MK-801 (10 µM) (n = 8, p < 0.05), but not the nAchR channel blocker chlorisondamine (20 µM). Furthermore, pretreatment of the neurons with the α7nAchR specific antagonist α-Bungarotoxin for 40 minutes inhibited the choline-induced synergistic effect.