Fig. 6.
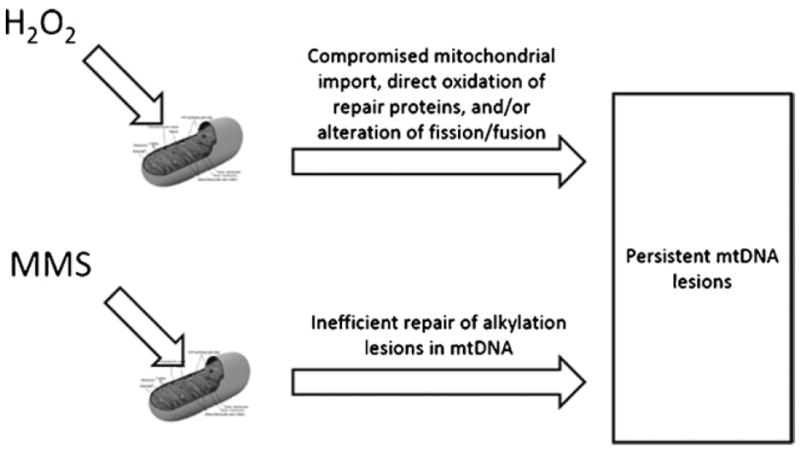
Model of mtDNA damage persistence in H2O2- versus MMS-treated cells. Mitochondrial DNA damage is predicted to persist in H2O2-treated cells due to oxidant-induced inhibition of mitochondrial protein import, direct oxidation of repair proteins, and/or perturbations in mitochondrial dynamics. MMS-induced mtDNA lesions are predicted to persist due to an insufficient alkylation repair pathway in mitochondria. As of yet, no proteins that recognize and repair alkylating lesions have been identified in mammalian mitochondria.
