Fig. 2.
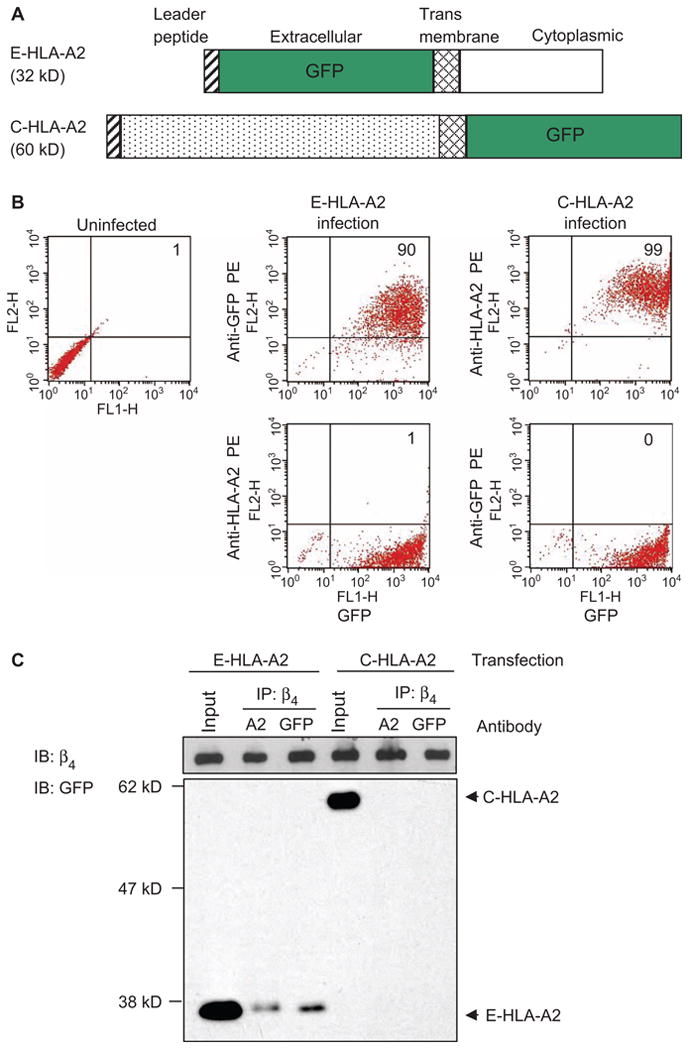
The cytoplasmic domain of the HLA-I heavy chain mediates the interaction between HLA-I and integrin β4. (A) Schematic representation of the mutant HLA-A2 molecules that have either the extracellular (E-HLA-A2) or the cytoplasmic (C-HLA-A2) domains deleted and replaced with GFP. (B) Endothelial cells were infected with adenoviruses encoding either E-HLA-A2 or C-HLA-A2. More than 90% of the infected cells contained the mutant proteins, as determined by flow cytometric analysis of GFP. Data are representative of 10 independent experiments. (C) Endothelial cells containing E-HLA-A2 or C-HLA-A2 were stimulated with antibodies against either HLA-A2 or GFP, cells were lysed and subjected to immunoprecipitation with Sepharose beads conjugated to antibody against integrin β4, and samples were analyzed by Western blotting with an antibody against GFP. Endothelial cells from donor EC2 were used in these experiments. For each sample, 10% of the total cell lysate used in the immunoprecipitation was loaded as an input control. Data are representative of three independent experiments.
