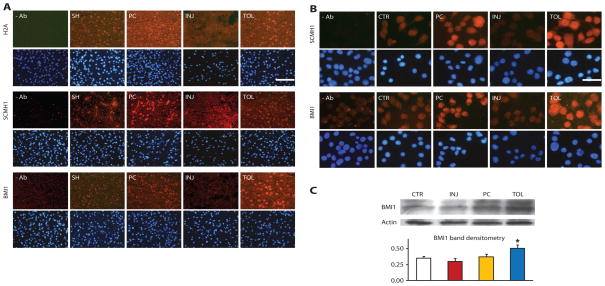
Fig. 2.
Differential changes of representative gene repressor proteins under different ischemic conditions in brains and cultured neuronal cells. (A) Immunohistochemical analysis of H2A, SCMH1, and BMI1 showed increased immunoreactivity (red) in ischemic-preconditioned (PC) and ischemic-tolerant (TOL) brains, relative to that in sham brains (SH), but decreased immunoreactivity in injured brains (INJ). Mice were subjected to the MCAO treatment paradigm described in Fig. 1. Bottom rows show DAPI staining (blue) to reveal nuclei. At least two brains of each condition were analyzed with similar results. The scale bar represents 50 μm. (B and C) Increased immunoreactivity of SCMH1 and BMI1 in NS20Y cells under simulated ischemic-tolerant (OGD-tolerant) conditions. Four groups of differentiated NS20Y cells were treated with the following conditions: (1) control (CTR); (2) preconditioning (PC); (3) injurious (INJ); (4) tolerant (TOL) (details are in Materials and Methods). Cells were then fixed and examined by immunocytochemistry for SCMH1 or BMI1 (B). BMI1 was also analyzed by Western blot (Western blot of actin serves as a loading control), with parallel analysis of actin (C, bottom) as a loading control. Similar results were obtained in at least three independent cultures. Scale bar, 25 μm. *P < 0.05.