Figure 2. Domain structure of cofilin and its main functions.
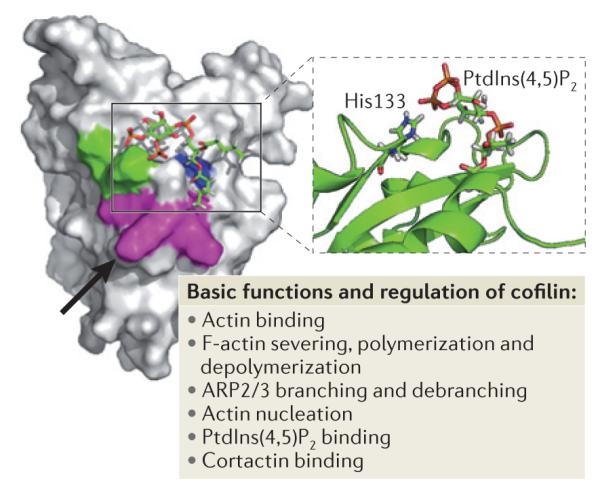
Key amino acids involved in the regulation of cofilin function are Asp122 and His133. The black arrow points to Asp122 located underneath Leu126 (in magenta). Asp122 regulates binding of cofilin to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphophate (PtdIns(4,5)P2). A cofilin mutant in which Asp122 has been replaced with Ala has increased binding affinity for PtdIns (4,5)P2 and this results in the inhibition of actin polymerization, cell protrusion and migration. His133 decreases cofilin affinity for PtdIns(4,5)P2 when deprotonated. Substitution of His133 with Ala in cofilin causes loss of H+ binding and increases steady-state actin polymerization and cell protrusion. Lys132 (which is involved in actin binding) and His133 are shown in green, Lys125, Lys126, and Lys127 (which are alternative residues for PtdIns(4,5)P2 binding) are shown in magenta and Phe15 and Leu99 are shown in blue. The figure is modified, with permission, from REF. 102 © (2008) Rockefeller University Press.
