Figure 1.
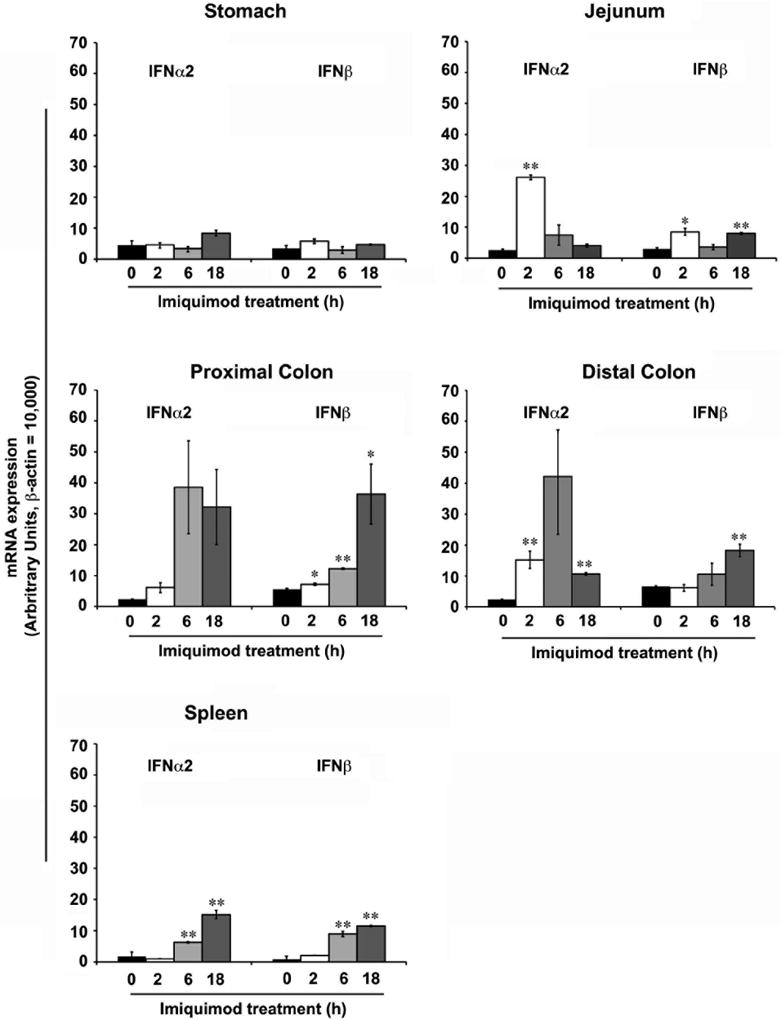
Imiquimod induces the expression of type I IFN in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Oral administration of Imiquimod (30 mg/kg body wt) to Balb/c mice exhibited differential induction in the expression of type I IFN (α, β) in various parts of the GI tract. In the stomach, no significant changes in the expression type I IFN were noted. In the jejunum, Imiquimod treatments led to significant increases in IFN-α2 and IFN-β expression at the 2 hours time point. In the proximal & distal colon treatments led to significant increases in both IFN-α2 and IFN-β expression at 6 &18 hours time points. Similar type I IFN induction was observed in spleen. N = 5; results represent the data from three individual experiments and expressed as the mean ± SEM (* P < .05; ** P < .01).
