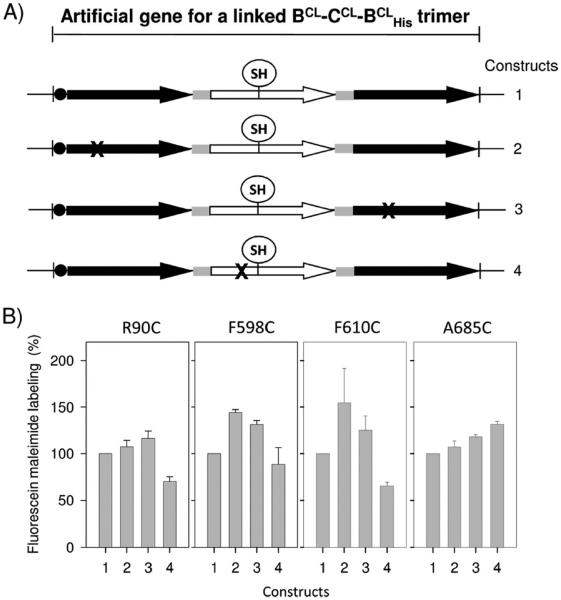
Figure 6.
Effect of proton translocation defect on the accessibility of cysteine substitutions of putative MdtC substrate-binding pocket residues to fluorescein 5-maleimide. A set of artificial constructs (labeled 2–4) in which one subunit of the single-cysteine MdtC mutant (R90C, F598C, F610C, and A685C) of the linked BCL–CCL–BCLHis trimer has a proton translocation mutation (D410A of the MdtB subunit or D401A of the MdtC subunit represented by X), together with a control construct containing no proton translocation mutation in any of its subunits (labeled 1), was constructed in the background of pSMA-BCLCCLBCL10. The mutant protein was expressed from each plasmid construct in BL21KAMR cells by IPTG (10 μM) induction. The cells were subjected to a labeling reaction with 40 μM fluorescein 5-maleimide, and the labeled proteins were purified. In each experiment, the protein sample was loaded into two different SDS–PAGE gels and the average of two normalized fluorescence intensities was obtained. The extent of labeling was expressed relatively as a percentage to that of the first construct shown. The means of at least three separate experiments are shown. Bars indicate the standard deviation.