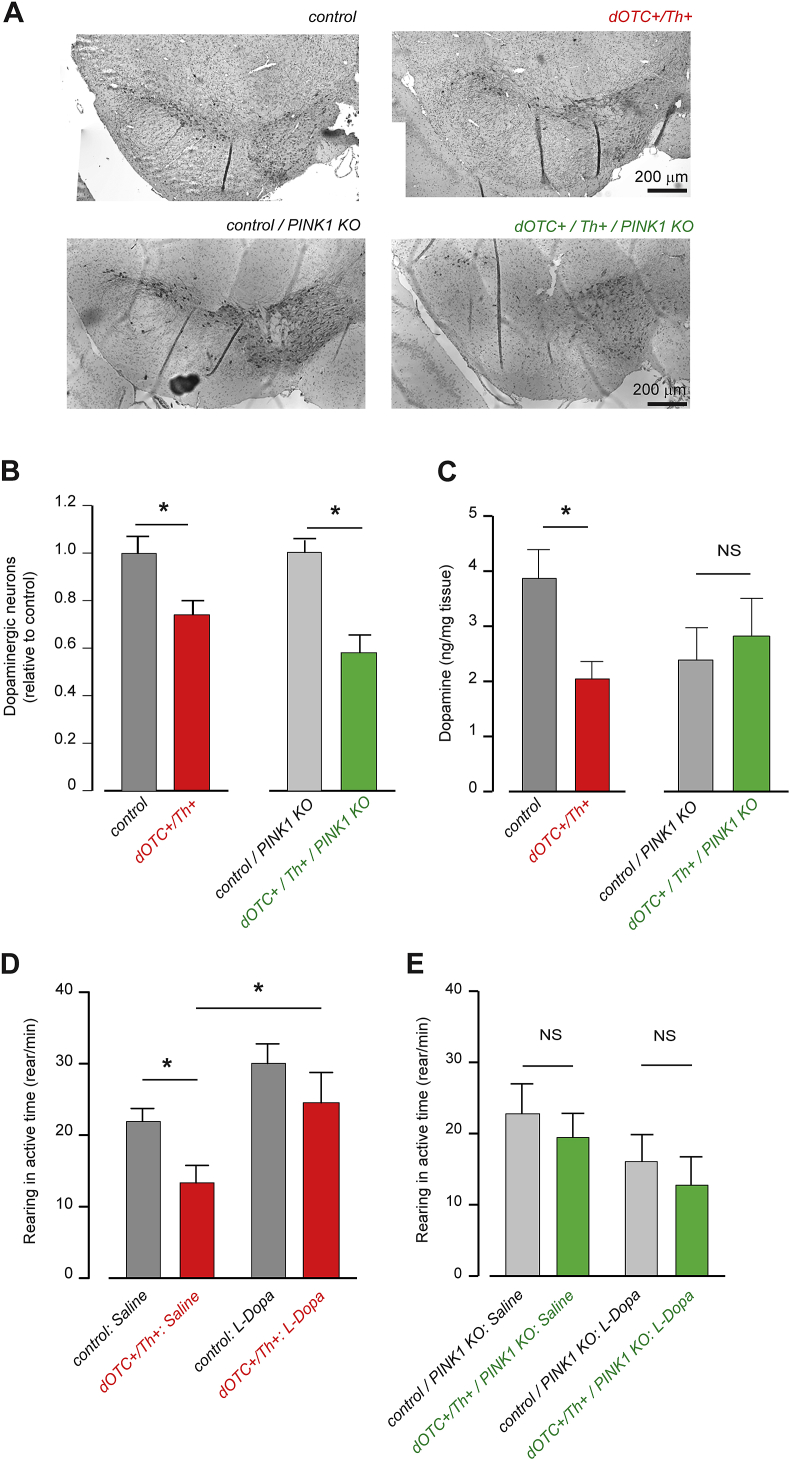
Fig. 4.
Neurodegeneration in the dopaminergic pathway. The neuronal cell death was assayed by immunohistochemistry of tyrosine hydroxylase positive neurons in brains of the indicated genotypes. Overexpression of dOTC induces cell death in the Substantia Nigra with a significant reduction in the dopaminergic neurons of 25% at one year of age (A, B) (n = 3). In the PINK1 KO background this decrease is accentuated as shown by a more severe reduction in the number of Th positive neurons, to 40% (n = 3) (C) The level of dopamine in Substantia Nigra was analysed by HPLC measurements in tissue of the indicated genotype. The dopamine content is reduced in the double transgenic in WT background, versus control. Overexpression of dOTC in PINK1 KO background does not decrease the dopamine level as compared to PINK1 KO control. (D) Pharmacological rescue of behavioural deficit with l-dopa shows increased activity in a population of mice from double transgenics in both control and dOTC overexpressing mice. The data presented here are from responsive mice (n = 4 WT, n = 3 PINK1 KO). (E) For triple transgenic mice with dOTC expressed in PINK1 KO background there is no response reflected in rearing activity changes following l-dopa treatment. (n = 8 for each WT and PINK1 KO). The analysis was performed with Student T-test between the indicated groups.