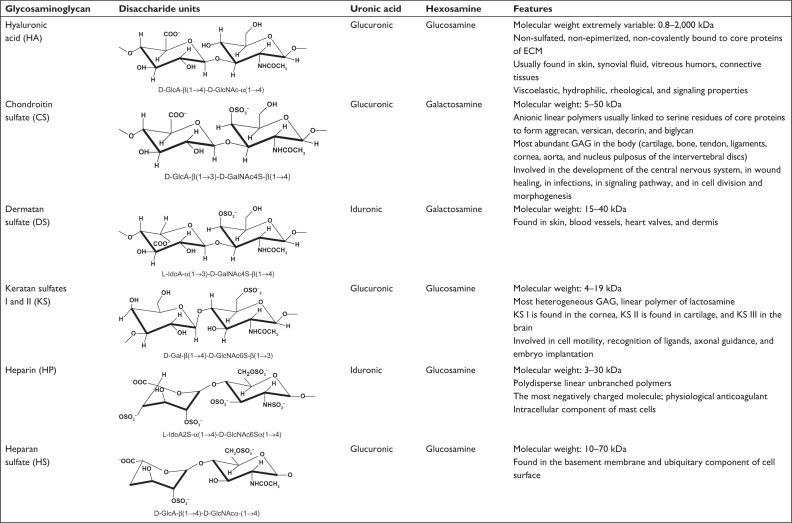
Figure 1.
Disaccharide units and carbohydrate sequences of the six main types of GAGs. The characterizing uronic acid and hexosamine are specified. Positions of sulfate groups are identified, showing that sulfate groups are more numerous in HP, followed by HS, CS, DS, and KS, and are absent in HA. The latter does not attach to proteins to form proteoglycans.
Note: Copyright© 2008, John Wiley and Sons. Reproduced with permission from Gandhi NS, Mancera RL. The structure of glycosaminoglycans and their interactions with proteins. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2008;72(6):455–482.2
Abbreviations: CS, chondroitin sulfate; DS, dermatan sulfate; ECM, extracellular matrix; GAG, glycosaminoglycans; HA, hyaluronic acid; HP, heparin; HS, heparan sulfate; KS, keratan sulfates.