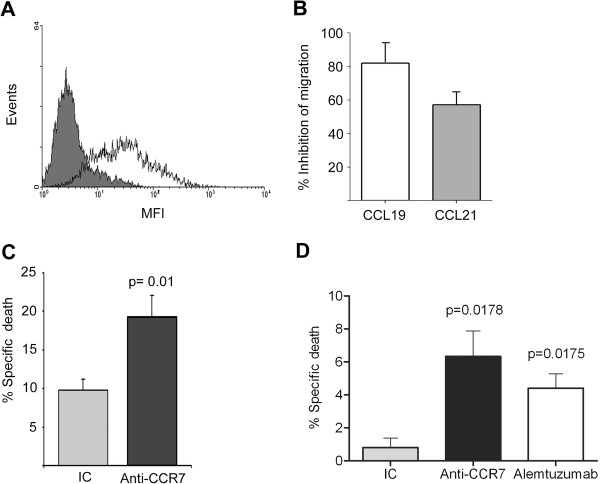
Figure 1.
In vitro mechanisms of action of anti-CCR7 mAb. (A) Expression of CCR7 on MCL cell line Granta-519 by flow cytometry. Cells were co-stained with anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody (mAb) and either isotype control mAb (grey area) or anti-human CCR7 mAb (white area). CCR7 surface density was measured as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). One representative experiment is shown. (B) Anti-CCR7 mAb abrogated the migration of Granta-519 cells. Cells were preincubated with anti-CCR7 mAb (2 μg/ml) or the respective irrelevant isotype control and then exposed to CCL19 or CCL21 for 4 hours in a transwell assay. (C) Anti-CCR7 mAb mediates specific CDC in Granta-519 cells. Cells were incubated with anti-CCR7 mAb (2 μg/ml) or the respective irrelevant isotype control (IC) and then exposed to rabbit complement for 1 h. Cell lysis was determined by 7-AAD incorporation in flow cytometry. The fold induction of cell lysis as a result of CDC is shown here. Bars represent mean +/- SD of six experiments. P-value refers to the difference of cell lysis fold induction mediated by an IC or an anti-CCR7 mAb. (D) Anti-CCR7 mAb mediates ADCC of Granta-519 cells. Calcein-UV-labeled Granta-519 cells previously incubated either with isotype control (IC), anti-CCR7 mAb (100 μg/ml) or alemtuzumab (100 μg/ml), were plated with human PBMC at an effector to target ratio of 10:1 for 24 hours. The average percentage of specific lysis +/- SEM from three independent experiments is shown. P-values refer to the differences of specific lysis mediated by anti-CCR7 mAb or alemtuzumab and the IC.